Getting your peptide dosage right is the bedrock of a safe and successful protocol. It's not a one-size-fits-all deal; the correct amount depends on the specific peptide you're using, your personal goals, and even factors like your body weight. For something like BPC-157, a starting point might be 200-500 mcg daily, while for Semaglutide, you might begin with just 0.25 mg weekly. The key is to start low and go slow, giving your body a chance to adapt before making any changes. Precision is everything here.
Understanding Peptides Before Your First Dose

Before you even think about mixing a vial or drawing up a dose, it’s critical to get a handle on what peptides are. A casual, uninformed approach isn't just ineffective—it's risky. Peptides are short strings of amino acids, which are the fundamental building blocks of proteins. You can think of them as tiny, highly specific messengers that signal your cells to perform certain jobs.
These powerful molecules can influence a huge range of bodily functions, which is why they’ve become so important in both medicine and wellness. Their ability to home in on specific cellular pathways makes them incredibly useful for everything from healing tissue and tamping down inflammation to supporting metabolism and promoting anti-aging effects.
The Critical Role of Purity and Stability
Here’s a hard truth: not all peptides are created equal. The safety and effectiveness of your entire protocol hinge on the purity and stability of the product you’re using. Peptides are fragile. They can easily be degraded by heat, rough handling, or improper storage. A degraded peptide is useless at best and could even trigger unwanted reactions at worst.
This is why your source is non-negotiable. Reputable suppliers will always provide third-party lab testing results to prove the purity of their products. This isn't just a marketing tactic; it's a fundamental safety standard.
Regulatory bodies set incredibly strict guidelines for peptide therapeutics, with allowable thresholds for impurities often falling between just 0.05% and 1%. This shows how medically important it is to use a pure, well-made product for predictable and safe outcomes.
Why Precision Is Everything
The explosion of interest in peptides is backed by serious medical and market growth. The global peptide therapeutics market was valued at an estimated $43.45 billion in 2023, and peptides accounted for about 9% of all new drug approvals by the US FDA between 2016 and 2023. These aren't just flashy numbers; they show that peptides are recognized as legitimate and powerful tools when used correctly. For a deeper dive, you can review the regulatory landscape and market data to see these industry standards for yourself.
This level of clinical integration is exactly why your approach has to be methodical. Every single step in this guide—from choosing the right peptide to calculating the dose and administering it—is designed to help you operate with that same precision. Getting the dose wrong can lead to serious issues:
- Ineffectiveness: Too low a dose, and you might not see any benefits at all, wasting both your time and your money.
- Side Effects: Too high a dose can overwhelm your system and trigger things like nausea, headaches, or fluid retention.
- Tolerance Issues: Starting with too high a dose can make your body less responsive to the peptide over time, diminishing its effects.
Taking the time to build this foundational knowledge first is what separates a responsible user from someone taking a gamble. It turns the process from a guessing game into a structured, informed strategy for safely reaching your health goals.
How to Reconstitute Peptides Correctly
An incorrectly prepared peptide is as good as no peptide at all. The process of reconstitution—mixing the freeze-dried powder (the lyophilized peptide) with a sterile liquid—is where many well-intentioned users go wrong. This isn't just a simple mix; it's a delicate procedure. The fragile peptide molecules can be easily damaged, rendering your carefully calculated dose ineffective before it's even drawn into a syringe.
Think of the lyophilized peptide as a delicate crystal structure. Your goal is to gently dissolve it, not shatter it. This requires the right supplies, a steady hand, and a bit of patience. Rushing this process is a guaranteed way to waste your investment and compromise your results.
Gathering Your Essential Supplies
Before you even think about mixing, get everything you need assembled in a clean, uncluttered space. Having all your tools ready to go prevents mistakes and ensures a sterile process from start to finish.
- Lyophilized Peptide Vial: This is the small glass bottle containing the peptide in its powder form.
- Bacteriostatic Water: This is the gold standard for reconstitution. It's sterile water containing 0.9% benzyl alcohol, which acts as a preservative to keep bacteria from growing after you've opened the vial.
- Alcohol Prep Pads: You'll use these to sanitize the rubber stoppers on your vials, a simple but critical step to prevent contamination.
- A Syringe for Mixing: A 1mL or 3mL syringe is perfect for drawing the bacteriostatic water and adding it to the peptide vial.
- A Syringe for Dosing: A U-100 insulin syringe (usually 0.3mL, 0.5mL, or 1mL) is what you'll use for administering the final dose. Never use the same syringe for mixing and dosing.
Having two separate, clearly designated syringes is a non-negotiable part of safe handling. This practice prevents cross-contamination and ensures your dosage measurements remain absolutely precise.
The Gentle Art of Reconstitution
With your supplies laid out, you're ready to mix. Let's walk through a common, real-world scenario: reconstituting a 5mg vial of BPC-157. The goal is to create a solution that's easy to dose from accurately.
First, gently pop the plastic cap off both the peptide vial and the bacteriostatic water vial. Use a fresh alcohol pad to wipe the rubber stopper on each one, then let them air dry for a moment. Don't skip this hygiene step; it's absolutely critical.
Next, you'll draw your chosen amount of bacteriostatic water into your mixing syringe. A common and practical choice is to use 1mL or 2mL of water. Using 2mL of water for a 5mg vial of BPC-157 is a popular method because it makes the math for dosing incredibly simple later on.
Now for the most important part. Slowly and carefully insert the needle of the mixing syringe through the rubber stopper of the peptide vial. Be sure to angle the needle so the stream of water runs gently down the side of the glass. Do not spray the water directly onto the peptide powder. That kind of force can damage the fragile peptide chains.
Key Takeaway: The goal is gentle rehydration, not forceful mixing. Let the water trickle down the inside wall of the vial. Once all the water is in, you can remove the syringe.
Finally, just gently swirl the vial or roll it between your palms. Never, ever shake it. Shaking is far too aggressive and will denature the peptides, making them useless. The powder should dissolve completely within a few minutes, leaving you with a clear liquid. For a more detailed breakdown of this process, check out our comprehensive guide on peptide mixing and dosage instructions.
Once dissolved, your peptide is ready for dosing and should be stored in the refrigerator to maintain its stability and potency.
Calculating Your Peptide Dose With Confidence
Once you've properly reconstituted your peptide, the next step is nailing the dosage. This is where precision really matters. Getting the dose just right is what separates getting the results you want from spinning your wheels. It might seem a little intimidating at first, but I promise the math is simple once you get the hang of it.
Let's ditch the guesswork. We're going to walk through the exact process, step-by-step, using real-world examples. My goal is to make you feel confident enough to draw up the correct amount every single time. You're simply translating a desired dose in micrograms (mcg) into a specific volume on your syringe.
To get started, you just need three pieces of information:
- The total amount of peptide in your vial (e.g., 5mg or 10mg).
- The amount of bacteriostatic water you added (e.g., 1mL or 2mL).
- Your desired dose based on your protocol (e.g., 250mcg).
With these three numbers, figuring out how much to draw into your syringe is a piece of cake.
The Foundational Dosage Formula
No matter what peptide you're using, the basic formula for calculating your dose is always the same. The main idea is to figure out the concentration of peptide in each unit of liquid. Once you know that, you can easily calculate how much liquid you need to get your target dose.
Let's break it down. Say you have a 5mg vial of BPC-157 and you reconstituted it with 2mL of bacteriostatic water. Your solution's concentration is 2.5mg per mL (5mg ÷ 2mL = 2.5mg/mL). Simple enough.
But here’s a pro tip: since most peptide doses are measured in micrograms (mcg), it's much easier to convert everything to mcg right from the start. Just remember that 1mg = 1000mcg.
So, that 5mg vial actually contains 5000mcg of peptide. When you add 2mL of water, the concentration becomes 2500mcg per mL (5000mcg ÷ 2mL). This number is the key to all your calculations.
Real-World Calculation Example 1
Let's put this into practice with a common scenario. You want to take a 250mcg dose of BPC-157 from your 5mg vial, which you've mixed with 2mL of water.
We already know the concentration is 2500mcg for every 1mL of liquid. A standard U-100 insulin syringe holds 1mL total, which is divided into 100 units. This means every 10 units on the syringe equals 0.1mL.
Here’s the thought process:
- Your vial has 5000mcg in 2mL of water.
- This means 1mL contains 2500mcg.
- Therefore, 0.1mL (which is 10 units on your syringe) must contain 250mcg.
Bingo. To get your 250mcg dose, you just need to draw the liquid up to the 10-unit mark on your U-100 syringe.
Real-World Calculation Example 2
Let’s try another one to build your confidence, this time with a different peptide and a larger dose. Imagine you need a 1mg dose from a 10mg vial of CJC-1295, also reconstituted with 2mL of water.
First, let's get all our units on the same page (micrograms).
- Vial Size: 10mg = 10,000mcg
- Desired Dose: 1mg = 1,000mcg
- Reconstitution Volume: 2mL
Now, find the concentration: 10,000mcg ÷ 2mL = 5,000mcg per mL.
Your target is a 1,000mcg dose. Since 1mL contains 5,000mcg, you know you'll need less than a full mL. Here's the simple math to find the exact volume:
(Desired Dose ÷ Concentration per mL) = Injection Volume
(1,000mcg ÷ 5,000mcg/mL) = 0.2mL
To find where 0.2mL is on your U-100 syringe, you just multiply by 100. That means you'll draw the solution to the 20-unit mark. See? Once you do it a couple of times, it becomes second nature.
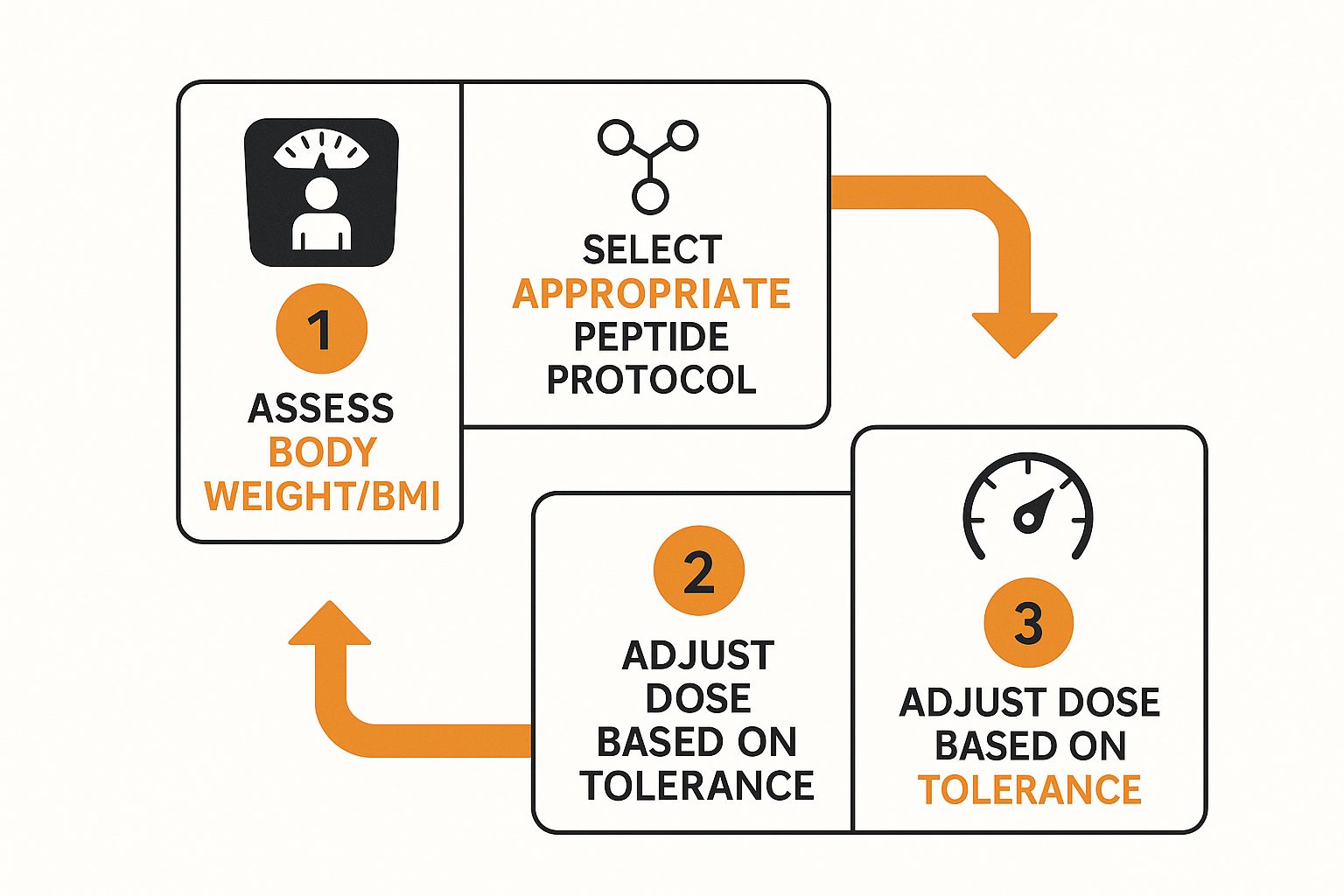
As this guide shows, calculating your peptide dose isn't just about the math. It's a personalized process that starts with your individual needs, moves to a specific protocol, and finishes with ongoing fine-tuning.
Quick-Reference Dosage Chart
To make life even easier, I've put together a quick-reference chart. It's a great way to skip the math for common dosages, especially if you're reconstituting your vials with a standard amount of water.
This table assumes you've reconstituted your peptide vial with exactly 1mL of bacteriostatic water.
| Quick Peptide Dosage Calculation Chart | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vial Size (mg) | Desired Dose (mcg) | Concentration per 0.1mL (mcg) | Injection Volume (Units on U-100 Syringe) |
| 2mg | 200mcg | 200mcg | 10 Units |
| 5mg | 250mcg | 500mcg | 5 Units |
| 5mg | 500mcg | 500mcg | 10 Units |
| 10mg | 500mcg | 1000mcg | 5 Units |
| 10mg | 1000mcg (1mg) | 1000mcg | 10 Units |
Remember, this chart is just a shortcut. It's always a good idea to understand the underlying math so you can dose confidently with any vial size or reconstitution volume.
Important Tip: Double-checking your math is never a bad idea. Using an online peptide calculator is a great way to confirm your own calculations, especially when you're just starting out. It gives you that extra peace of mind.
By mastering this simple math and using helpful tools like the chart above, you can approach every single dose with complete confidence. This attention to detail is what sets you up for a safe and successful experience.
Safe and Effective Administration Techniques
Perfecting your dosage calculation is a huge step, but the journey doesn't end there. Proper administration is just as critical for ensuring the peptide works as intended without causing unnecessary issues. While there are a few delivery methods out there, the one you’ll most likely be using for self-administration is a subcutaneous injection.
This just means injecting the peptide into the fatty layer of tissue right beneath the skin. It’s the go-to method because it’s relatively simple, minimally painful, and allows for a slow, steady absorption of the peptide into your system. Once you get the hang of it, the whole process becomes routine and safe.
Choosing and Rotating Your Injection Sites
One of the most important habits you can build is injection site rotation. I can't stress this enough. Using the same tiny spot over and over is a recipe for problems like lipohypertrophy—a buildup of scar tissue and fat under the skin. This hardened tissue can seriously mess with how well your body absorbs the peptide and often leads to irritation.
To sidestep this, you need to cycle through different areas of your body. The best sites are those with a decent layer of subcutaneous fat.
- Abdomen: This is a popular choice because it’s easy to reach and has a large surface area. Just be sure to inject at least two inches away from your belly button.
- Thighs: The outer or front part of the thigh is another excellent, easy-to-reach option with plenty of fatty tissue.
- Glutes: The upper, outer part of your buttocks is also a good spot, though it can be a bit harder to reach on your own.
- Upper Arms: The fatty area on the back of the upper arm works well, but you might need a hand from someone else to inject here properly.
Here’s a simple trick I tell people: imagine your abdomen is a large clock face. One day you can inject at the 1 o'clock position, the next at 3 o'clock, and so on, always staying at least an inch away from the last spot. This easy system makes sure no single area gets overused.
The Injection Process, Step by Step
Walking through the injection process can make it feel much less intimidating. Once you get the steps down, it’s a quick and straightforward procedure.
First things first, preparation is key. Wash your hands thoroughly. Grab a fresh alcohol prep pad and vigorously clean the rubber stopper of your refrigerated peptide vial, then let it air dry completely.
Next, draw up your dose. Use a new, sterile U-100 insulin syringe to pull up your calculated amount. After drawing, flick the syringe gently to get any big air bubbles to the top, and then carefully push the plunger to expel them.
Now, sanitize the site. Pick your injection spot and clean a small area of skin (about two inches across) with another fresh alcohol pad. Again, let it air dry. Don't rush this part.
Time to administer the injection. Gently pinch a fold of skin at the sanitized site. Holding the syringe like a dart, insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle. For most people, a 90-degree angle is fine, but if you're very lean, a 45-degree angle helps ensure you’re in the fat layer and not the muscle.
Finally, inject and withdraw. Slowly and steadily push the plunger down until the syringe is empty. Wait a few seconds, then pull the needle out at the same angle you put it in. Immediately and safely dispose of the syringe in a designated sharps container.
Non-Negotiable Rule: Always use a brand new, sterile syringe for every single injection. Reusing needles is a major safety risk that can lead to infection, contamination of your peptide vial, and blunted needles that cause more pain and tissue damage.
The frequency of these injections is often dictated by the peptide’s half-life and your specific protocol. Injectable peptides can require dosing intervals anywhere from daily to monthly, while other forms like oral peptides are generally dosed more often because they break down faster. You can explore more about how delivery technology impacts dosing schedules to get a deeper understanding of the science. This knowledge reinforces why sticking to your specific protocol's timing is so important for seeing results.
Real-World Peptide Dosing Protocols

Theory is one thing, but seeing how dosing strategies actually play out in the real world is where the confidence comes from. This is where we pull it all together—reconstitution, calculation, and administration—into practical, goal-oriented protocols for some of today's most common peptides.
Keep in mind, these aren't rigid prescriptions. They're common starting points based on extensive clinical experience. The fundamental principle of any effective peptide protocol remains the same: start low and titrate slowly. This approach lets you see how your body uniquely responds, helping you find that sweet spot where benefits are high and side effects are low.
A Protocol for Healing with BPC-157
Let's kick things off with BPC-157, a true workhorse peptide for injury recovery and gut health. Its versatility makes it a staple for everyone from athletes nursing a torn ligament to individuals looking for relief from nagging gut inflammation.
A typical starting protocol for BPC-157 is built around a daily dose to keep stable levels in the body, which helps promote consistent healing signals.
- Common Starting Dose:250mcg to 500mcg per day.
- Administration Frequency: This total daily amount is often split into two separate injections (e.g., 250mcg in the morning and 250mcg in the evening).
- Injection Site: For localized injuries like tendonitis in the elbow, subcutaneous injections near the site are common. For systemic benefits like gut repair, a standard abdominal injection works perfectly fine.
- Typical Cycle Duration: A cycle usually runs from 4 to 6 weeks. This is generally enough time to notice significant improvements in tissue repair and reduced inflammation.
This split-dosing strategy helps maintain more consistent levels of the peptide in your system, which can be a game-changer for supporting ongoing healing processes.
Dosing for Weight Management with Semaglutide
Semaglutide has quickly become a major tool for metabolic support and weight management, but its protocol is a masterclass in the importance of gradual dose escalation. Jumping to a high dose too quickly is a surefire way to get hit with significant side effects like nausea.
The standard approach is a slow titration schedule, giving your body weeks to adapt to each new level. Semaglutide, first approved in 2017, is a prime example of why precise dosing is so critical in clinical practice. It's typically given as a subcutaneous injection starting at 0.25 mg weekly and has a long half-life of about seven days thanks to its unique chemical structure. For more intensive weight management, doses can be increased up to 2.4 mg weekly, showing how dosing is carefully adjusted for different goals. For a deeper scientific dive, you can explore an analysis of how Semaglutide's dosage is tailored for clinical outcomes.
Here’s what a typical titration schedule might look like:
| Weeks | Weekly Dose | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-4 | 0.25mg | Acclimation Phase |
| Weeks 5-8 | 0.5mg | Initial Titration |
| Weeks 9-12 | 1.0mg | Continued Titration |
| Weeks 13+ | 1.7mg – 2.4mg | Therapeutic Dose |
This slow-and-steady progression is the key to a successful and tolerable experience, allowing you to find the lowest effective dose for your needs. If you're interested in this area, you can learn more about how different peptides can be used for weight loss in our dedicated guide.
Stacking for Synergistic Effects: Ipamorelin and CJC-1295
Stacking, or using multiple peptides together, is a common strategy to create synergistic effects that are greater than the sum of their parts. The classic stack for anti-aging, muscle growth, and recovery is Ipamorelin combined with CJC-1295 (without DAC).
These two peptides work on the same pathway but in slightly different ways, prompting a strong, natural pulse of growth hormone release from the pituitary gland.
A key insight for this stack is timing. Administering these peptides before bed aligns the induced growth hormone pulse with your body’s own natural nighttime peak, potentially amplifying the restorative effects on sleep and recovery.
A common protocol for this powerful duo looks like this:
- Ipamorelin Dose:100-200mcg per injection.
- CJC-1295 (no DAC) Dose:100mcg per injection.
- Frequency:1 to 2 times per day. A pre-bedtime injection is the most popular approach. Some users add a second injection post-workout or first thing in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Cycle Duration: Cycles often run for 8 to 12 weeks, followed by a break to ensure the pituitary gland remains responsive.
These real-world examples prove there is no "one-size-fits-all" answer. Your ideal protocol is a personal formula derived from the peptide's characteristics, your specific goals, and most importantly, your body's individual response. Approach your own protocol with this same informed, safe, and patient strategy.
Common Questions About Peptide Dosing
When you're starting with peptides, it's totally normal to have a few questions pop up. In fact, getting these practical details ironed out is what separates a confusing experience from a confident one. Let's walk through some of the most common situations you might run into so you know exactly how to handle them.
Think of this as your practical FAQ. Knowing what to do ahead of time takes the guesswork out of the equation and keeps you on the right track.
What Should I Do If I Miss a Peptide Dose?
First off, don't panic. Missing a dose happens to everyone, and it’s not a big deal as long as you handle it correctly. The key is to avoid overcompensating. How you proceed really depends on the peptide’s half-life.
If you’re on a daily peptide like BPC-157 or Ipamorelin, you can usually take your missed dose as soon as you remember. However, if you’re already getting close to your next scheduled injection, just skip the one you missed and get back on your normal schedule.
Crucial Tip: Never double up on your next dose to "catch up." This doesn't help you reach your goals faster and significantly bumps up the risk of side effects. Consistency over time is what drives results.
For peptides with a longer-lasting effect, like weekly Semaglutide, you have a lot more wiggle room. You can typically take the missed dose as long as your next one is still more than two or three days away. If it's closer than that, it's best to just skip it and wait for your next planned day.
How Do I Know If My Peptide Dosage Is Correct?
Figuring out your ideal dose isn't about hitting a magic number; it's a process of listening to your body. The "right" dosage is simply the amount that delivers the results you want with few or no side effects.
Your body will give you the feedback you need. Are you noticing the benefits you’re after—like faster recovery, less inflammation, or better sleep? Just as importantly, are you free from nagging issues like headaches, nausea, or feeling bloated from water retention?
This is where keeping a simple log becomes your best friend. Jot down your dose, the time you took it, and any effects you feel, both good and bad. If side effects are a constant issue, your dose is almost certainly too high. On the flip side, if you've given it enough time and feel absolutely nothing, a very slow, methodical increase might be in order. Ultimately, the question of is peptide therapy safe is closely tied to responsible dosing and paying attention to your body’s signals.
Can I Mix Different Peptides in the Same Syringe?
While you might hear about people doing this, mixing peptides in the same syringe is generally not recommended, especially if you're new to this. The biggest concern is chemical stability. When you combine different peptide molecules, you risk them interacting in a way that degrades them, making one or both less effective.
There are, of course, a few well-documented exceptions. The popular stack of Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 (without DAC) is a classic example. These are often mixed because they are known to be stable together and are meant to be administered at the same time for a synergistic effect.
But unless you’re following a specific protocol from a trusted medical professional who has explicitly stated that two peptides are safe to combine, the best practice is to play it safe. Using a separate, sterile syringe for each peptide is the gold standard. It completely removes any doubt about chemical reactions and guarantees that every dose you take is pure, stable, and precisely measured.
At Elite Bioscience, we provide the highest quality, third-party tested therapies to support your health goals. Explore our tailored peptide and vitamin packages to start your journey with confidence.







