What is Testosterone Cypionate? Complete Guide & Benefits

Testosterone cypionate is a supplemental, long-acting form of the natural testosterone your body produces. When a doctor prescribes it for conditions like hypogonadism, it's used to restore hormone levels and ease the symptoms that come with low testosterone.
Think of it like topping off your car's engine oil. When a key fluid is low, the engine sputters and struggles. By adding more, you're not replacing the engine—you're just bringing an essential fluid back to the optimal level so everything can run smoothly again.
Understanding Testosterone Cypionate Without the Jargon
At its core, testosterone cypionate is a bioidentical hormone attached to something called a cypionate ester. This structure is the key to how it works. The testosterone part is chemically identical to what your body makes naturally, but the ester acts like a time-release coating on a pill. It allows the hormone to enter your bloodstream slowly and steadily over time.
This controlled release is what really sets it apart from other forms. Instead of creating sharp spikes and sudden drops in your hormone levels, it provides a much more stable and predictable supply. This approach means you need less frequent injections—usually just once a week or every two weeks—while still maintaining consistent therapeutic effects. The goal is simple: bring your hormone levels back into a healthy, balanced range.
To give you a quick summary, here are the core characteristics of this treatment.
Testosterone Cypionate At a Glance
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Hormone Type | Bioidentical Testosterone |
| Ester | Cypionate (Long-acting) |
| Administration | Intramuscular Injection |
| Release Mechanism | Slow and sustained over time |
| Typical Frequency | Weekly or bi-weekly |
| Primary Use | Medically diagnosed hypogonadism (low T) |
This table shows how each element works together to create a stable, effective therapy for restoring hormonal balance under medical supervision.
The Core Concept Visualized
This infographic helps illustrate how your body's natural testosterone and a cypionate supplement work together to restore hormonal balance.
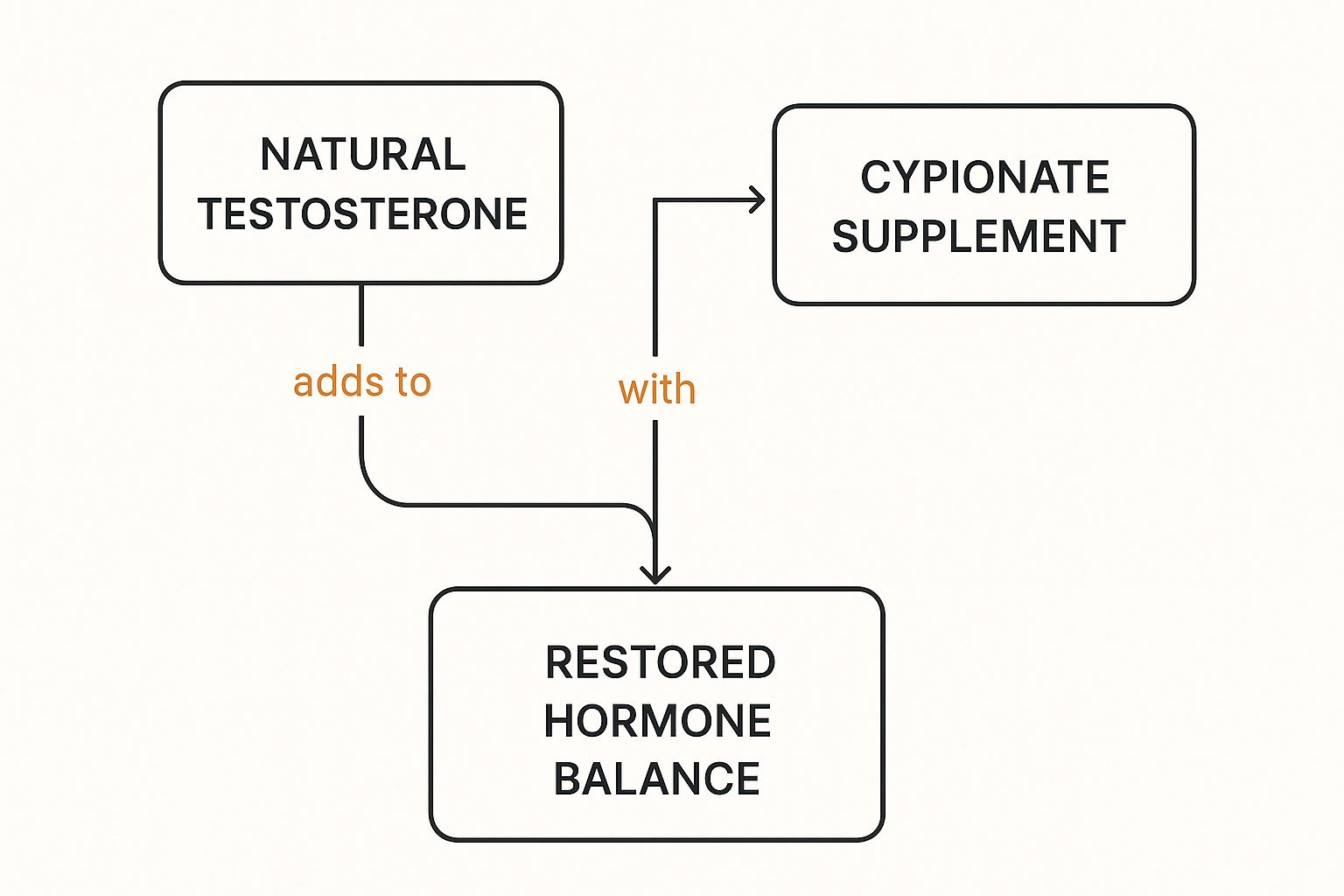
As you can see, the therapy doesn't shut down your body's own production. It just supplements it to bridge the gap and get you back to a state of equilibrium.
Why This Treatment Is Medically Necessary
Let's be clear: testosterone cypionate is not a casual supplement or a performance booster for athletes. It is a medically prescribed treatment for diagnosed health conditions, most notably hypogonadism—a condition where the body simply fails to produce enough testosterone on its own.
Symptoms that often lead a doctor to diagnose this include:
- Persistent Fatigue: A constant feeling of being drained that isn't fixed by a good night's sleep.
- Cognitive Issues: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or that frustrating "brain fog."
- Mood Changes: An increase in irritability, unpredictable mood swings, or feelings of depression.
- Low Libido: A noticeable drop in sexual desire and performance.
The need for effective treatments has grown significantly. The market for testosterone cypionate was valued at $3.41 billion and is projected to climb to $5.76 billion in the coming years. This reflects a growing awareness of hypogonadism and an aging population seeking solutions. You can explore the full market analysis to understand these trends better.
The ultimate goal of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) with cypionate is to restore physiological hormone levels. The aim is to improve quality of life, energy, mood, and overall well-being—all under strict medical supervision.
By understanding what testosterone cypionate is and its intended medical purpose, you can have a much more informed conversation with your healthcare provider about whether this therapy is the right path for your specific health needs.
How Testosterone Cypionate Actually Works in Your Body

When you inject testosterone cypionate, it doesn’t just hit your system like a tidal wave. Instead, it uses a clever, time-delayed process to give you a steady, predictable supply of testosterone. Think of it as a slow-drip irrigation system for your body—it delivers exactly what’s needed, right where it’s needed, without causing the hormonal floods and droughts you'd get from raw, unmodified testosterone.
The real magic is in its molecular design. What you're injecting is bioidentical testosterone with a chemical "tail" attached to it, known as the cypionate ester. This ester is the component that turns a short-acting hormone into a long-lasting therapy.
Once the testosterone cypionate is injected into a muscle, it creates a small reservoir, or depot. From here, it doesn't rush into your bloodstream. It seeps out slowly and steadily. As it enters circulation, enzymes in your body get to work, neatly snipping the cypionate ester off the testosterone molecule.
This happens gradually. Once that ester is gone, you’re left with pure, bioidentical testosterone, which your body recognizes and uses just like the testosterone it makes naturally.
The Role of the Cypionate Ester
So, what does that little ester tail actually do? It’s essentially a built-in timer. It controls the release rate of the active hormone, preventing your body from metabolizing and flushing it out too quickly.
Without the ester, you'd need constant doses to keep your levels stable. The ester’s presence is what ensures a sustained release over several days, making a convenient dosing schedule of once every 7 to 14 days possible. This steady delivery is the key to getting consistent results and avoiding the side effects tied to wild hormone swings.
The cypionate ester’s job is simple but critical: it slows down testosterone’s absorption and breakdown. This extends the hormone's life in your system, creating a gradual release that better mimics your body's natural rhythm.
By carefully managing this release, testosterone cypionate helps maintain stable blood levels. This stability is the bedrock of effective low testosterone treatment, supporting everything from your energy and mood to muscle mass and bone density.
Understanding Half-Life and Its Impact
To really get a feel for how long testosterone cypionate sticks around, you need to understand the concept of half-life. A drug’s half-life is simply the time it takes for half of the initial dose to be cleared from your body.
Testosterone cypionate has a half-life of roughly 7 to 8 days. This means a full week after your injection, about half of the dose is still active in your system. This relatively long half-life is exactly why weekly or bi-weekly injections are so effective for TRT.
Let’s walk through its journey inside your body, step-by-step:
- Injection: The testosterone cypionate is injected into a muscle, where it pools to form a depot.
- Slow Release: Over the next several days, the ester allows the testosterone to be absorbed slowly from the muscle into your bloodstream.
- Metabolism: Your body’s enzymes snip off the cypionate ester, activating the testosterone.
- Action: This free testosterone now travels throughout your body, binding to androgen receptors and influencing cells in your muscles, bones, brain, and other critical systems.
- Clearance: Over the course of the week, your hormone levels gradually taper down as the medication is processed and eventually eliminated.
This controlled cycle ensures your body gets a consistent and reliable supply of testosterone. The end result is a more balanced hormonal environment, allowing you to feel the full benefits of therapy without the jarring ups and downs of hormone spikes. It's this predictable, steady mechanism that makes testosterone cypionate a cornerstone of modern testosterone replacement therapy.
Medical Reasons for Prescribing Testosterone Cypionate
First things first: testosterone cypionate is a serious medical treatment, not a lifestyle supplement you can pick up over the counter. It’s prescribed by a doctor only after a thorough evaluation, which includes identifying clear clinical symptoms and confirming them with blood tests. This careful process ensures the therapy is both necessary and safe for the patient.
The single most common reason a doctor will write a prescription for it is hypogonadism. It’s the medical term for a condition where the body simply can’t produce enough testosterone on its own. The problem can lie with the testicles themselves or with the brain's command centers—the pituitary gland and hypothalamus—which are supposed to tell the testicles to get to work.
Think of it like a factory production line. If the factory floor (the testicles) is damaged, production grinds to a halt. On the other hand, if the head office (the brain) never sends the production orders, the factory sits idle. Either way, testosterone output plummets, triggering a cascade of disruptive symptoms.
Identifying Primary Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism is when the problem is right at the source: the testicles. They get the right signals from the brain, but for some reason, they just can’t respond. It’s like flipping a working light switch, but nothing happens because the bulb itself is burnt out.
This issue can be traced back to several causes:
- Genetic disorders that impact how the testicles develop or function.
- Physical injury or direct trauma to the testicles.
- Medical treatments like chemotherapy or radiation, which can unfortunately damage testicular cells.
- Undescended testicles that weren’t corrected during childhood.
In these situations, testosterone cypionate acts as a direct replacement. It bypasses the malfunctioning factory and delivers the finished product right where it’s needed to get the body back in balance.
Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism is a different kind of breakdown—it’s a communication problem. The testicles are perfectly fine and ready to produce testosterone, but they aren’t getting the memo from the brain’s pituitary gland. The factory is fully operational, but management isn’t sending down the work orders.
This signaling failure is often linked to:
- Pituitary disorders, such as tumors or inflammation that disrupt hormone signals.
- Certain medications that can interfere with the body's hormonal feedback system.
- Obesity, as excess body fat can throw the body's natural hormone loops out of whack.
- Chronic illness or severe stress, both of which can suppress the brain’s signaling functions.
When a doctor diagnoses secondary hypogonadism, they might prescribe testosterone cypionate to restore hormone levels immediately. This helps alleviate the patient's symptoms and improve their quality of life while the doctor investigates the root cause of the signaling issue.
The goal of prescribing testosterone cypionate is never about achieving superhuman levels. It’s about returning a patient to a healthy, normal physiological range to resolve debilitating symptoms like chronic fatigue, low libido, mood instability, and brain fog caused by the deficiency.
The injectable segment of the testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) market, which includes this medication, generates the highest revenue. Testosterone cypionate alone accounted for $636.1 million in market revenue and is projected to grow steadily over the next decade. You can discover more insights about the growth of the testosterone cypionate injection market to see its established role in medicine.
Ultimately, a prescription for testosterone cypionate is the final step in a clear diagnostic process. It starts with a patient reporting persistent symptoms, is confirmed by conclusive blood tests, and results in a targeted treatment plan designed to fix a documented medical problem. If you are struggling with these symptoms, you can learn more about the various low testosterone treatment options available under proper medical supervision.
Navigating Dosing and Administration Safely
Figuring out the right dose of testosterone cypionate isn't a guessing game. It's a highly personal process, and there’s no magic number that works for everyone. Your healthcare provider acts like a skilled navigator, using your blood work, symptoms, and health goals as their map.
The objective isn't to chase the highest possible number on a lab report. It's about restoring your testosterone to an optimal range where your symptoms fade and you genuinely feel your best.
This is a journey of fine-tuning. What works perfectly for one person might be too much or too little for another, which is exactly why ongoing medical supervision is the cornerstone of safe and effective therapy.
Establishing Your Personalized Dosing Protocol
When you first start, your doctor will set an initial dose based on clinical guidelines and your lab results. Think of this as a starting point, not the final destination. It's designed to gently introduce the hormone and see how your body responds.
A common starting schedule might be an injection once a week or every two weeks. This is based on testosterone cypionate's 7-to-8-day half-life, which allows for a steady, predictable release into your system. Some clinicians even prefer more frequent, smaller injections—like twice a week—to keep blood levels extra stable and smooth out any hormonal peaks and valleys.
A few weeks after you begin, your provider will schedule follow-up blood tests. These are critical for seeing how your body is using the medication, allowing your doctor to make precise, data-driven adjustments.
Your testosterone cypionate dosage is a dynamic figure, not a static one. It will likely be fine-tuned by your doctor based on routine blood work and how you feel, ensuring the therapy remains optimized for your unique physiology.
This methodical calibration ensures you get the exact amount of testosterone your body needs to thrive without triggering unnecessary side effects. For a closer look at how these schedules work, our guide on a typical TRT dosage per week offers some great insights.
The Practical Side of Administration
Testosterone cypionate is delivered via an intramuscular (IM) injection, which means the medication goes deep into a muscle. This method creates a small reservoir, or depot, allowing the testosterone to be slowly absorbed into your bloodstream over several days.
Using the proper technique is essential for safety, comfort, and getting the most out of your treatment. Your healthcare provider will give you detailed instructions, but knowing the basics can help you feel more confident.
Common injection sites include:
- Gluteal Muscles (Glutes): The upper, outer part of the buttock is a large, dense muscle, making it a popular and effective spot.
- Vastus Lateralis (Thigh): This is the large muscle on the outer side of your thigh. It's another common location that’s easy to access yourself.
- Deltoid Muscle (Shoulder): The deltoid can be a good site for smaller injection volumes, though it's a smaller muscle.
A sterile environment is non-negotiable. Always use a brand new, sterile needle and syringe for every injection, and clean the site thoroughly with an alcohol swab before and after. It's also a smart practice to rotate your injection sites to prevent any tissue scarring or long-term discomfort.
Ultimately, this information is meant to empower you for productive conversations with your medical team, not to serve as a do-it-yourself guide. Safe and successful testosterone therapy is built on a strong partnership between an informed patient and an experienced healthcare provider.
Weighing The Benefits Against Potential Side Effects
Embarking on any medical treatment requires a clear-eyed view of both the potential rewards and the possible risks. Testosterone cypionate therapy is no different. The ultimate goal is to restore hormonal balance, and when done right, the improvements to your quality of life can be absolutely night and day.
However, a responsible approach means understanding the full picture. It's about appreciating the life-changing benefits while also respecting the potential side effects—and recognizing the critical need for ongoing medical supervision to keep everything on track.

The Positive Impact Of Restored Testosterone Levels
When your testosterone levels are brought back into a healthy, optimal range, the benefits often directly counteract the very symptoms that brought you to your doctor in the first place. Think of it as putting the foundation of your well-being back on solid ground.
Under proper medical supervision, many men report a cascade of positive changes.
- Renewed Energy and Vitality: That persistent, bone-deep fatigue that often defines low T can finally lift. It's replaced by a renewed sense of energy and drive to actually engage with life again.
- Improved Mood and Mental Clarity: Brain fog and irritability frequently start to fade, giving way to sharper focus, better concentration, and a much more stable, positive mood.
- Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone is a key player in muscle protein synthesis. Restoring your levels can make it easier to build and maintain lean muscle, especially when you’re putting in the work with regular exercise.
- Enhanced Libido and Sexual Function: A noticeable drop in sexual desire is a hallmark symptom of low testosterone. Therapy can often bring a healthy libido roaring back and improve overall sexual performance.
- Better Bone Density: Testosterone is crucial for maintaining bone strength. Over the long term, TRT can help protect against age-related bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
These improvements don’t happen overnight. While you might feel a shift in mood and energy within a few weeks, physical transformations like increased muscle mass can take several months to become fully apparent.
Understanding The Potential Side Effects
Just as you need to know the upside, it's equally crucial to be aware of the potential side effects. The good news is that most are manageable and can be minimized with proper dosing and regular monitoring by your healthcare provider.
The side effects can be broken down into two main categories: the more common (and milder) issues and the less frequent but more serious considerations.
Common and Generally Mild Side Effects
These are issues that many men might experience, particularly when first starting therapy, but they can often be handled with simple adjustments from your doctor.
- Injection Site Reactions: You might notice some soreness, redness, or swelling right where you injected. This is usually temporary and can be lessened by simply rotating your injection locations.
- Acne or Oily Skin: An increase in testosterone can sometimes kick your skin's oil glands into higher gear, leading to breakouts similar to what you might have experienced during puberty.
- Fluid Retention: Some guys notice a bit of mild swelling, particularly in the ankles or feet, as the body adjusts to the new hormone levels.
It's absolutely vital to keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider. Reporting any side effects promptly allows them to make small tweaks to your protocol, ensuring your treatment stays both safe and effective.
For a more detailed breakdown, you can learn more about the complete range of testosterone therapy side effects in our comprehensive guide.
Less Common but More Serious Considerations
These are the risks that underscore why testosterone cypionate must always be used under strict medical supervision. Regular blood work is the primary tool your doctor uses to keep an eye out for these potential issues long before they can become problems.
- Changes in Cholesterol: Testosterone can sometimes affect your lipid profile, potentially lowering HDL ("good") cholesterol. Your doctor will monitor this closely.
- Increased Red Blood Cell Count: TRT can stimulate your bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. While this can boost endurance, if the count gets too high (polycythemia), it can thicken the blood and increase the risk of clotting.
- Prostate Health: For men with a pre-existing, undiagnosed prostate issue, testosterone therapy could potentially stimulate its growth. This is exactly why thorough screening before and during therapy is non-negotiable.
Potential Benefits vs Potential Risks of Testosterone Cypionate
Navigating testosterone therapy is all about balance. This table gives you a clear, side-by-side look at the potential positive outcomes and the side effects you need to consider with your doctor.
| Potential Benefits | Potential Side Effects and Risks |
|---|---|
| Increased energy and reduced fatigue | Acne or oily skin |
| Improved mood, focus, and mental clarity | Injection site soreness or redness |
| Enhanced libido and sexual function | Mild fluid retention |
| Easier to build and maintain muscle mass | Changes in cholesterol levels (lower HDL) |
| Stronger bone density over the long term | Increased red blood cell count (polycythemia) |
| Decreased body fat when paired with diet & exercise | Potential stimulation of prostate tissue |
The key to navigating this landscape safely is a strong partnership between you and your doctor. Your job is to follow your prescribed protocol and report any changes you notice. Your doctor’s role is to use their expertise and your lab results to keep your treatment perfectly calibrated—maximizing all the benefits while keeping any risks in check.
Your Questions About Testosterone Cypionate Answered
Jumping into testosterone replacement therapy can bring up a lot of practical questions. To give you clear, straightforward answers, this section covers the most common things people ask when first learning about testosterone cypionate. My goal here is to be direct and informative, helping you build a solid understanding.
How Long Does It Take to Feel the Effects of Testosterone Cypionate?
The timeline for feeling the benefits of testosterone cypionate is different for everyone. It’s a gradual process, not an overnight fix, because your body needs time to adjust to restored hormone levels.
Many guys start to notice initial improvements in mood, energy, and libido within the first 3 to 6 weeks of consistent therapy. These early shifts are often the first sign that the treatment is starting to hit its mark.
However, the more significant physical changes take a bit longer to show up.
- Increased Muscle Mass: Changes in body composition, like building lean muscle, typically become noticeable after about 3 to 6 months of medically supervised treatment.
- Improved Bone Density: The benefits to bone health are more of a long game, with measurable improvements often seen after six months or more.
Patience is key here. Keeping an open line of communication with your doctor will help you track your progress and know what to expect as your therapy continues.
Is Testosterone Cypionate Better Than Other Forms of TRT?
The idea of a single "best" form of TRT is a common myth. Testosterone cypionate isn't automatically better than other options, but it is different, offering specific advantages that can fit certain lifestyles and medical needs. Its main feature is the slow-acting cypionate ester, which allows for a convenient weekly or bi-weekly injection schedule.
The most effective TRT option is the one that aligns best with your individual health profile, lifestyle, and your doctor's expert recommendation after a complete evaluation.
Other forms of testosterone therapy include:
- Topical Gels or Patches: Applied to the skin every day.
- Long-Acting Pellets: Implanted just under the skin every few months.
- Short-Acting Esters: These require more frequent injections.
Each method has its own unique set of pros and cons. The right choice is always a personalized medical decision made with your doctor.
Is Testosterone Replacement Therapy a Lifelong Commitment?
For many men, especially those with chronic conditions that cause hypogonadism, TRT is a long-term or even lifelong treatment. The therapy works by giving your body the testosterone it can no longer produce on its own.
If you stop the treatment, your testosterone levels will almost certainly drop back to their previously low baseline. As a result, the original symptoms of low T—like fatigue, low libido, and mood swings—will come back. Any decision to start, pause, or stop therapy has to be made in close partnership with your healthcare provider.
At Elite Bioscience, we provide the expert guidance and high-quality therapies you need to restore your vitality safely. Explore your personalized treatment options by visiting us at https://elitebioscience.co.
QUICK SEARCH
Make an account today to start your journey towards a better and healthier lifestyle.






