What Actually Are Peptides? Your Foundation For Smart Decisions
To figure out if peptide therapy is safe, we first need to understand what peptides are. Think of them as your body’s internal text messaging system. They are short chains of amino acids, which are the basic building blocks of proteins. While a protein might be a long, detailed email, a peptide is like a short, direct text message—a specific command sent from one group of cells to another.

These cellular messages are incredibly precise. A peptide designed to kickstart skin repair won’t accidentally tell your muscles to grow. This targeted action is what makes them so promising in modern medicine. Unlike some traditional drugs that can have widespread, unintended effects, therapeutic peptides are designed to mimic the body’s natural communication pathways. They essentially “speak the body’s language,” leading to a focused effect with a lower risk of unexpected reactions. This specificity is a core reason many consider peptide therapy safe under proper medical guidance.
How Therapeutic Peptides Differ From Natural Ones
Your body naturally produces thousands of different peptides every day to manage everything from digestion and mood to sleep and inflammation. However, as we age or face certain health issues, our natural peptide production can slow down. This is where therapeutic peptides come into play.
These are lab-created versions of natural peptides, often with slight tweaks to make them more stable and effective. For example, some are modified to last longer in the bloodstream, giving them more time to deliver their message before being broken down. This modification is key to making peptide therapy a practical treatment option.
The safety and effectiveness of these treatments are not just theories; they are supported by extensive research and regulatory oversight. As of 2025, more than 100 peptides have received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for therapeutic use. An additional pipeline of nearly 1,000 other peptides is currently in various stages of clinical trials, showing ongoing scientific confidence. You can explore detailed information on FDA-approved peptides and ongoing trials to learn more about the regulatory landscape.
Common Types of Peptides and Their Functions
The world of peptides is diverse, with different types serving different roles. To help you better understand their safety and applications, we’ve organized the most common peptide types into the table below.
Common Therapeutic Peptides and Their Safety Classifications
A breakdown of the most frequently used peptide categories in clinical practice, their mechanisms of action, and established safety profiles.
| Peptide Type | Primary Function | Common Applications | Safety Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth Hormone Peptides | Stimulate natural growth hormone release | Muscle growth, fat loss, anti-aging, enhanced recovery | Generally well-tolerated under medical supervision; some risk of water retention or joint pain. |
| Healing & Repair Peptides | Accelerate tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation | Muscle/tendon injuries, wound healing, gut health (e.g., BPC-157, TB-500) | Considered very safe with minimal side effects; often mimics the body’s natural repair signals. |
| Immune-Modulating Peptides | Regulate immune system function | Autoimmune conditions, chronic infections, inflammation control | Varies by peptide; typically requires careful medical oversight to avoid over- or under-stimulation of the immune system. |
| Cosmetic Peptides | Stimulate collagen and elastin production | Anti-wrinkle creams, skin firming, hair growth | High safety profile for topical use; low risk of systemic side effects. |
| Nootropic Peptides | Support cognitive function and brain health | Memory enhancement, improved focus, neuroprotection | Emerging field; safety profiles are still being established but generally considered safe in studied doses. |
This table shows how different peptides are designed for specific tasks, from healing injuries to improving skin. For instance, healing peptides like BPC-157 and Thymosin Beta-4 are known for their targeted action on tissue repair and have a strong safety record. You can learn more about how one of these peptides works in our guide on TB-500, a key peptide for muscle regeneration and enhanced recovery.
By understanding these categories, it becomes clear that the safety of a peptide is closely linked to its specific function and how it interacts with the body’s natural systems.
The Real Numbers: What Clinical Data Reveals About Safety
Moving beyond theory, the best way to answer the question, “is peptide therapy safe?” is to look at how it performs in the real world. When we analyze clinical data from thousands of patients, a clear and reassuring picture emerges. This isn’t about hand-picking good results; it’s about seeing the complete safety profile when peptides are used by diverse groups of people in medical settings.
This type of investigation is called post-marketing surveillance, where treatments are monitored after they are approved for general use. Think of it like testing a new car model not just on a perfect track, but across thousands of miles of real city streets, highways, and bumpy country roads with all kinds of drivers. This real-world evidence is critical because it shows how a therapy holds up amid the complexities of daily life, including in patients with other health conditions or those taking other medications.
Insights from Large-Scale Studies
When we examine this broader data, the safety of many therapeutic peptides is remarkably strong. For instance, a major post-marketing safety study on placental polypeptide injections offers compelling evidence. The research followed 3,000 patients with an average age of nearly 50, a group often dealing with multiple health factors. Even with many patients taking other medications at the same time, the adverse drug reaction (ADR) rate was an incredibly low 0.03%. Only one case of vertigo was reported out of the entire group. You can read the full research about these clinical findings to review the detailed analysis.
Data like this is fundamental. It shows that even in a large, varied patient group with complex medical histories, the therapy maintained an exceptional safety record. This supports the idea that the targeted action of peptides, which we covered earlier, often leads to minimal side effects in clinical practice. Their specific action lowers the risk of unintended consequences, a common concern with more systemic conventional drugs.
Comparing Peptides to Conventional Treatments
Another way to understand safety is by comparing peptide therapy to more traditional pharmaceuticals. While every effective treatment has some level of risk, the side effects for many peptides are often milder and happen less frequently. This is because peptides are “biomimetic”—they mimic the body’s own signaling molecules. It’s like using a key designed for a specific lock (the peptide) versus using a crowbar (a less targeted drug). The key opens the door with almost no disruption, while the crowbar might get the job done but will likely cause other damage.
This precision is clear in adverse event databases. Where conventional drugs for similar conditions might list dozens of common side effects, many peptide therapies only report minor, localized issues like temporary redness at the injection site. This distinction underscores why so many clinicians are confident in prescribing them.
Of course, this excellent safety profile depends on several key factors:
- Correct Dosing: Giving the right amount is crucial to prevent unwanted effects.
- Patient Screening: A complete medical evaluation ensures the patient is a good candidate.
- Peptide Quality: Using pure, pharmaceutical-grade peptides from a reputable source is essential.
When these best practices are followed under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider, clinical data overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that peptide therapy is a safe and effective choice for many people.
Side Effects Decoded: What To Expect And When To Worry
Any honest discussion about peptide therapy must include a look at potential side effects. While these treatments are generally well-tolerated because they mimic the body’s own signaling molecules, they are not entirely without risk. The good news is that most reported reactions are mild and temporary, often just a sign that your body is adapting.
Think of it like starting a new workout routine—you expect some muscle soreness as your body adjusts. In the same way, peptide therapy can cause temporary reactions as your cellular systems respond to new instructions. Understanding the difference between a normal adjustment and a real warning sign is key to a safe and effective experience.
Common Reactions and Their Significance
Most side effects are manageable and often resolve on their own as your body gets used to the treatment. The most frequently reported issues are typically localized and minor.
Here’s what you might encounter:
- Injection Site Reactions: This is the most common reaction, presenting as redness, mild swelling, itching, or soreness right where you administer the shot. It’s usually a localized immune response that fades within a few hours.
- Increased Hunger: Certain peptides, particularly those that stimulate growth hormone, can temporarily ramp up your appetite. For those using peptides for weight management, you can learn more about how specific peptides help by understanding appetite regulation.
- Water Retention: Some people might notice temporary fluid retention or a feeling of puffiness, especially in their hands and feet. This is often an early response to growth hormone-releasing peptides and typically subsides.
- Fatigue or Lightheadedness: As your body adjusts its metabolic or hormonal pathways, feeling a bit tired or lightheaded can occur. This is usually short-lived.
This bar chart visualizes the incidence rates of the most common, mild side effects associated with peptide therapy.
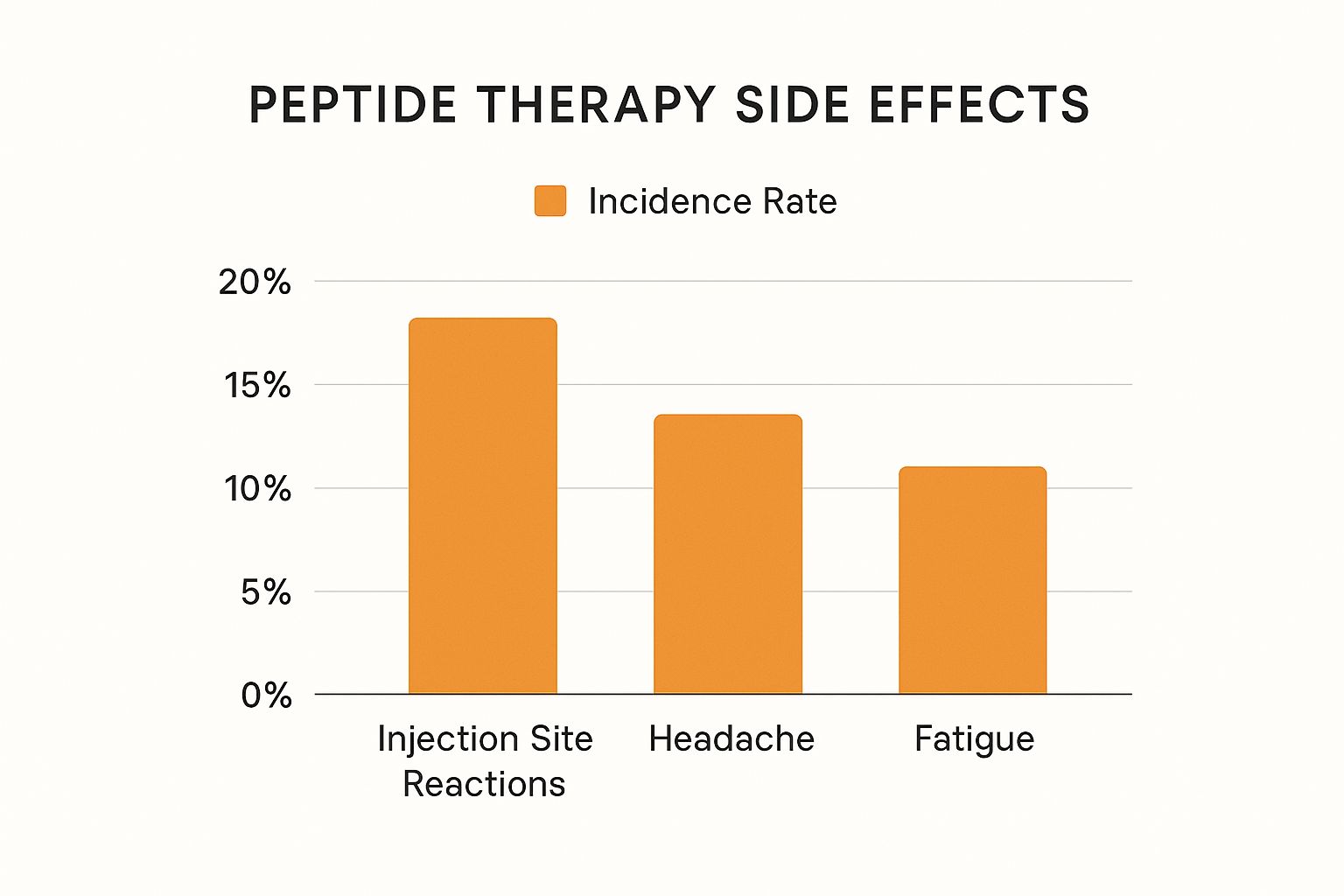
As the chart illustrates, these common side effects are relatively infrequent. Minor injection site reactions lead the pack, affecting about 20% of users, but most other side effects are far less common.
To give you a clearer picture, this table breaks down the most discussed side effects, their typical frequency and severity, and how they’re managed.
Peptide Therapy Side Effects: Reality Check And Management
A comprehensive overview of reported side effects, their actual occurrence rates, and evidence-based approaches for prevention and management.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Severity Level | Management Strategy | When to Seek Help |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Site Reaction | Common (~20%) | Mild | Rotate injection sites; apply a cool compress; ensure proper injection technique. | If pain is severe, swelling spreads, or a rash develops. |
| Increased Hunger | Occasional | Mild to Moderate | Adjust meal timing; increase protein and fiber intake; monitor calorie intake. | If it leads to uncontrollable eating or significant weight gain. |
| Water Retention | Occasional | Mild | Stay hydrated; reduce sodium intake; gentle exercise like walking. | If swelling is severe, sudden, or accompanied by shortness of breath. |
| Headache/Dizziness | Infrequent | Mild | Ensure adequate hydration; rest; avoid sudden movements. | If headaches are severe, persistent, or accompanied by vision changes. |
| Nausea | Infrequent | Mild to Moderate | Take peptide with food or before bed; start with a lower dose and increase slowly. | If nausea is severe, leads to vomiting, or prevents eating/drinking. |
| Allergic Reaction | Rare | Severe | Immediate medical attention required. | Hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. |
This table shows that while side effects are possible, the most common ones are mild and easily managed. Severe reactions are very rare but require immediate attention.
When To Contact Your Doctor
While mild reactions are common, more significant side effects are rare but demand attention. It’s crucial to know the difference between a minor bodily adjustment and a sign that something is wrong. For instance, in a 2023 trial with 411 adults using a GLP-1 peptide agonist, the treatment completion rate was high at 77%. However, adverse events were the main reason for discontinuation, accounting for 14% of those who stopped. You can read the full research about these safety findings to see the detailed breakdown.
You should contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent pain, swelling, or rash at the injection site.
- Signs of an allergic reaction, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Extreme or prolonged fatigue, dizziness, or nausea.
- Significant, unexplained joint or muscle pain.
Ultimately, peptide therapy is safe for most people when done under medical supervision. The key is to work with a qualified provider who can select the right peptide and dose for you, monitor your progress, and help you manage any side effects that arise.
Red Flags: When Peptide Therapy Isn’t Right For You
While peptide therapy offers remarkable benefits for many, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. The safest and most responsible choice is sometimes to say “no,” and a qualified healthcare provider will be upfront about situations where this treatment isn’t appropriate. Understanding these contraindications is essential for your well-being and empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
Think of your body’s health as a complex ecosystem. Introducing a powerful signaling molecule like a peptide can have unintended consequences if the environment isn’t right. This is why a thorough screening process is non-negotiable for determining if peptide therapy is a safe path for you.
Key Contraindications and Precautions
Certain medical conditions, life stages, and medications act as significant red flags, making peptide therapy inadvisable or requiring special modifications. A responsible provider will always conduct a deep dive into your medical history before starting any treatment.
Here are some of the most critical situations where caution is paramount:
- Active Cancer or History of Cancer: Because some peptides stimulate cell growth and proliferation, they are generally not recommended for individuals with active cancer. Those with a history of cancer must undergo a rigorous evaluation with their oncologist and peptide specialist to weigh the risks.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The effects of most therapeutic peptides on fetal development and infants are not well-studied. To ensure the safety of both mother and child, peptide therapy is strictly avoided during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
- Autoimmune Conditions: For individuals with autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, introducing peptides that affect the immune system requires extreme caution. The goal is to balance the system, not overstimulate it, which could worsen the condition.
- Serious Medical Conditions: Those with severe kidney or liver disease, or uncontrolled diabetes, may not be suitable candidates. The body’s ability to process and eliminate the peptides could be compromised, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
The Importance of a Thorough Medical Evaluation
The decision to start peptide therapy should never be taken lightly or based on a quick online quiz. A qualified provider will perform a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
- Detailed Medical History: Discussing past and present health conditions, surgeries, and family medical history.
- Current Medication Review: Analyzing all prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements to check for potential negative interactions.
- Baseline Blood Work: Obtaining crucial lab tests to assess organ function, hormone levels, and inflammatory markers.
This meticulous screening process is your primary safety net. It ensures that the proposed therapy aligns with your unique health status and goals. Cutting corners on this evaluation is a dangerous gamble, which is why working with a credentialed medical professional is the most important step in safely exploring peptide therapy.
Finding Qualified Providers: Your Safety Depends On This Choice
The safety of your peptide therapy experience doesn’t just rest on the peptide itself—it depends heavily on who provides it and where it comes from. Think of it like this: even the most advanced aircraft is only as dependable as its pilot and the quality of its fuel. Similarly, your results and safety depend entirely on your provider’s expertise and the integrity of the product. This decision is the single most important factor you control.

Trying to find the right provider can feel difficult, especially with the growth of online clinics and wellness centers. However, a few key markers separate truly qualified professionals from questionable sources. Your first step should be to find a licensed medical professional who has specific training in hormone and peptide therapies.
What to Look for in a Provider
A trustworthy provider is more than just someone with a prescription pad. They are a true partner in your health who understands the detailed science behind these treatments. When you are assessing a potential clinic or doctor, look for these non-negotiable credentials:
- Medical Licensing: The provider must be a licensed medical doctor (MD), doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), or a nurse practitioner (NP) working under a physician’s supervision.
- Specialized Training: Look for practitioners with experience in endocrinology, age management, or functional medicine. These fields often include deep education on peptide science.
- A Comprehensive Approach: A qualified provider will require a thorough initial consultation, including a detailed medical history and baseline blood work, before ever prescribing a peptide.
- Transparent Sourcing: They should be able to clearly explain where their peptides come from and show proof of their purity and potency.
This careful screening process ensures the answer to “is peptide therapy safe?” is a confident “yes” because it’s being managed correctly from the start.
The Critical Importance of Peptide Sourcing
The quality of the peptide is just as vital as the provider’s skill. The market is unfortunately filled with products labeled for “research purposes only,” which are not regulated and can be dangerous. These substances are not meant for human use and may contain impurities, incorrect dosages, or completely different compounds.
Using these non-pharmaceutical grade peptides is like fueling your car with a mysterious liquid from an unlabeled can—you have no idea what’s inside or what damage it might do. To ensure your safety, your peptides must come from a legitimate source.
Here’s a breakdown of what to look for:
| Source Type | Description | Safety Level |
|---|---|---|
| Compounding Pharmacies | U.S.-based pharmacies that create customized medications under strict state and federal regulations. They follow quality control and testing standards. | High |
| FDA-Approved Brands | Specific peptides, like Teriparatide (Forteo®), that have gone through the full FDA approval process for particular conditions. | Highest |
| “Research Chemical” Sites | Online vendors selling peptides not intended for human consumption. These are unregulated and carry significant risks of contamination and wrong dosing. | Extremely Low / Unsafe |
Ultimately, your safety is protected by choosing a medical provider who sources exclusively from reputable compounding pharmacies or uses FDA-approved products. They will make sure the “fuel” for your body is pure, potent, and exactly what it is supposed to be. By focusing on both a qualified expert and a high-quality product, you build the foundation for a successful and safe therapy journey.
Your Safety Protocol: Best Practices That Actually Work
Success with peptide therapy goes far beyond just getting a prescription. The real secret to unlocking benefits while staying safe is sticking to a proven protocol. Think of it like a blueprint for a house—even with the best materials, you won’t get a sturdy structure without following the instructions. These best practices shift you from a passive patient to an informed, active participant in your health journey.
Proper Handling and Administration
The first step in any safe peptide protocol starts before the peptide even enters your body. How you handle and administer it is crucial for its effectiveness and for minimizing any potential issues.
- Storage is Key: Most peptides are delicate molecules. They need to be kept refrigerated to maintain their stability and power. Storing them at the wrong temperature can make them completely ineffective.
- Hygienic Practices: Always use a fresh, sterile syringe for every single injection. Be sure to clean both the injection site and the vial’s top with an alcohol swab to prevent infection.
- Rotation of Injection Sites: To avoid skin irritation, soreness, or tissue buildup, it’s important to rotate where you inject. Common spots for subcutaneous injections include the abdomen, thighs, and glutes.
Following these simple yet critical steps helps ensure that every dose is both safe and effective.
The Role of Monitoring and Lifestyle Adjustments
Answering the question, “is peptide therapy safe?” for the long haul involves consistent monitoring. Your provider will set up regular follow-up appointments and blood tests to see how your body is responding. These tests check things like hormone levels and inflammatory markers to make sure the therapy is working as intended without creating imbalances.
Beyond the clinic, your daily habits play a massive part. Fine-tuning these lifestyle factors can dramatically improve your safety and results:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet high in protein provides the amino acid building blocks that peptides need to do their job, especially for muscle repair or fat loss. If you have specific goals, like exploring peptides for weight loss, a supportive diet is essential to see the best outcomes.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can multiply the effects of many peptides, particularly those designed to improve body composition and speed up recovery.
- Sleep: Your body does most of its repair work while you sleep. Recovery-focused peptides work best when you get at least 7-8 hours of quality, restorative sleep each night.
By weaving these practices into your routine, you create the ideal environment for peptides to work efficiently, putting you in the driver’s seat of your treatment’s success and safety.
Making Your Decision: A Realistic Safety Framework
After exploring the science, potential side effects, and professional standards, you now have the tools to make a truly informed choice about peptide therapy. This isn’t about following a trend or making a decision based on incomplete information; it’s about carefully weighing the evidence against your unique health profile. The answer to “is peptide therapy safe?” isn’t a simple yes or no—it’s a personalized conclusion you arrive at by partnering with a qualified expert. This final step is about creating a practical framework to see if this approach aligns with your goals.
The Personal Safety Checklist
Before moving forward, it’s wise to run through a personal safety checklist. This process helps turn abstract knowledge into concrete, actionable steps, making sure you’ve covered all your bases. Think of it as your final pre-flight check before taking off on your health journey.
- Have I had a comprehensive consultation? This is non-negotiable. It must involve a thorough review of your medical history, current medications, and a detailed discussion of your health goals with a licensed medical professional.
- Has baseline blood work been completed? A responsible provider will never prescribe peptides without first evaluating your hormone levels, organ function, and key inflammatory markers.
- Do I understand the specific peptide recommended for me? You should be clear on its intended purpose, the benefits you can expect, and the most common side effects linked to it.
- Have I verified the source of the peptides? Make sure your provider sources from a reputable, U.S.-based compounding pharmacy that follows strict quality and purity standards.
Answering “yes” to these questions builds a strong foundation for a safe and effective experience. If you find yourself answering “no” to any of them, consider it a major red flag that warrants a serious conversation with your provider before proceeding.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
Your consultation should be a two-way street. To be an active partner in your own care, you need to come prepared with the right questions. This promotes transparency and helps you assess your provider’s expertise and dedication to your well-being.
Your Essential Questions:
- Based on my specific health history and blood work, what particular risks should I be aware of with this therapy?
- What is your protocol for monitoring my progress and safety, including follow-up appointments and lab tests?
- What are the most common side effects you observe in your patients using this peptide, and how do you typically manage them?
- If I start to experience a side effect, what is the best way to contact you, and what signs would require immediate medical attention?
A trustworthy provider will not only welcome these questions but will also provide clear, direct answers. Their response should give you confidence, not just in the treatment itself, but in the support system you’ll have along the way. By combining your research with professional guidance, you can make a decision that puts your safety first while you work toward your health goals.
Ready to see if peptide therapy is right for you? At Elite Bioscience, we connect you with licensed medical professionals for a comprehensive evaluation and provide access to high-quality, third-party tested therapies. Take the first step toward your goals by completing our confidential health assessment today. Start your journey with Elite Bioscience.







