Understanding Injectable Vitamins: Beyond The Wellness Hype
While intravenous (IV) vitamin drips and nutrient shots are getting a lot of attention in wellness circles, their real purpose is often misunderstood. Injectable vitamins for humans aren't a new fad; they are a well-established medical tool used to deliver essential nutrients directly into the bloodstream, completely avoiding the digestive system. This difference is key.
Imagine your digestive tract is a long, winding road with tolls and checkpoints. When you take a vitamin pill, it travels this road, facing stomach acid and intestinal walls. Along the way, only a portion of its nutrients might actually make it to the final destination. An injection, however, is like taking a direct flight—it ensures near-total bioavailability, meaning almost 100% of the vitamin is immediately ready for your body to use.
The Science Of Bypassing Digestion
For people with conditions like Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or for those who've had gastric bypass surgery, the digestive "road" is full of roadblocks. Oral supplements may pass through their system with very little absorption, making them ineffective. In these situations, injectable vitamins are not a lifestyle choice but a clinical necessity. They prevent severe deficiencies that could lead to serious health problems.
This medical need is a major reason for the sector's growth. The global market for multivitamin injections was valued at about USD 3.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to more than double by 2032. This shows its growing importance in patient care. For a deeper look, you can explore market analysis of injectable vitamin trends to understand its clinical significance.
This diagram shows a typical intravenous therapy setup, the main method for giving many injectable vitamins.

The image illustrates how a vitamin-rich solution flows directly into a vein, allowing it to enter the circulatory system immediately.
Medical Necessity Versus Wellness Trend
It's important to know the difference between a medical requirement and a wellness preference. While IV lounges market injections for hangovers, jet lag, or an energy boost, their most critical role is clinical.
For a patient with pernicious anemia who can't absorb vitamin B12 through their gut, regular injections are life-saving. For someone with a severe vitamin D deficiency that doesn't improve with oral supplements, an injection can restore their levels much more effectively. The wellness industry has adopted this powerful medical tool, but its origins and most vital uses are firmly based on solving genuine health challenges, not just improving a healthy lifestyle.
How Your Body Actually Processes Injectable Vitamins
When you swallow a vitamin pill, it begins a long and tricky journey through your digestive system. Imagine sending a message through a series of checkpoints, where parts of it get lost or distorted at each stop. The harsh acid in your stomach, various digestive enzymes, and the liver's filtering processes all take a piece of the action. As a result, only a fraction of the nutrient actually makes it to your bloodstream. This concept is called bioavailability—it's the percentage of a substance that enters your circulation and can have an active effect. For many oral supplements, this number can be much lower than you'd think.
However, injectable vitamins for humans take a completely different path. They're like having a VIP pass that lets you skip the entire digestive maze. By delivering nutrients directly into a muscle (intramuscular) or a vein (intravenous), they achieve nearly 100% bioavailability. This direct route means the full dose is immediately available for your cells to use, leading to a much more efficient and predictable result. This is a key reason why they are a go-to method in medical settings for correcting deficiencies.
The First-Pass Effect: The Digestive Tollgate
One of the biggest obstacles for oral vitamins is the first-pass effect, also known as first-pass metabolism. After a nutrient is absorbed from your gut, it's immediately routed to the liver before it can enter your main circulatory system. The liver, acting as your body's primary filtration plant, metabolizes and breaks down a large portion of many substances, including vitamins. This "toll" can significantly reduce the amount of the active vitamin that gets to do its job. Injectable vitamins for humans completely sidestep this metabolic checkpoint, ensuring the intended dose is delivered intact.
The graph below shows how intravenous delivery leads to 100% bioavailability, while other methods result in lower and more delayed absorption.
As you can see, the intravenous (IV) route provides instant and complete access to the bloodstream, which is vital when addressing an urgent deficiency.
Why Direct Delivery Is Sometimes Necessary
For some people, this direct delivery method isn't just about efficiency—it's absolutely essential.
- Malabsorption Syndromes: Individuals with conditions like Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or atrophic gastritis have digestive systems that can't properly absorb nutrients from food or pills. For them, oral supplements are often like trying to fill a leaky bucket.
- Surgical History: Patients who have undergone certain gastrointestinal surgeries, such as a gastric bypass, have a smaller surface area for absorption. This makes injections a more reliable way to get the nutrients they need.
- Severe Deficiencies: When someone is severely deficient in a nutrient like vitamin B12 or vitamin D, correcting it quickly is critical. Injections provide the immediate, high-potency dose needed to restore health without delay.
In the end, whether oral or injectable vitamins are better for you depends on your body's specific needs and its ability to process them. While pills are effective for many, injections offer a dependable alternative when the digestive path is compromised or too slow.
Types Of Injectable Vitamins And When You Need Them
Not all injectable nutrients do the same job. Think of it like a mechanic's toolbox: you wouldn't use a wrench to change a tire. Similarly, healthcare providers select specific injectable vitamins for humans to address distinct health issues. This choice is a careful decision based on a person's individual health needs and body chemistry.
When most people hear "injectable vitamin," Vitamin B12 often comes to mind. While it's known for providing a quick energy lift, its clinical purpose is much more serious. For someone with pernicious anemia—a condition where the body cannot absorb B12 from food—these injections are not just beneficial; they are a lifeline. Without them, severe and irreversible nerve damage can occur. B-complex injections, a blend of several B vitamins, are also used to support nerve health and metabolism in people with confirmed deficiencies, not just for a general feeling of wellness.
Common Formulations and Their Clinical Roles
The world of injectable vitamins extends far beyond the B-group. Each type is used in situations where its direct delivery into the body provides a clear advantage over oral pills.
To help clarify the options, the table below outlines some of the most common injectable vitamins, their typical concentrations, and their specific medical uses.
| Vitamin Type | Common Concentration | Primary Uses | Administration Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) | 1,000 mcg/mL | Treating pernicious anemia, severe B12 deficiency, nerve support. | Intramuscular (IM) |
| B-Complex | Varies (blend) | Addressing multiple B-vitamin deficiencies, supporting metabolism. | Intramuscular (IM) |
| Vitamin D (Cholecalciferol) | 50,000 IU/mL | Correcting severe deficiency, especially with malabsorption issues. | Intramuscular (IM) |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 500 mg/mL | Supporting immune function and wound healing in clinical settings. | Intravenous (IV) |
| Vitamin K1 (Phytonadione) | 2 mg/mL or 10 mg/mL | Preventing bleeding in newborns; reversing anticoagulant effects. | Intramuscular (IM) or Subcutaneous (SQ) |
As you can see, the method and reason for using each vitamin are highly specific. An injection is chosen when the digestive system can't be relied upon to deliver the nutrient effectively, making it a powerful tool in a clinical setting.
- Vitamin D: While sunshine and pills work for most, severe deficiencies can weaken bones, leading to conditions like osteomalacia. For those with malabsorption problems, a high-dose Vitamin D shot can quickly bring levels back to normal and protect the skeleton.
- Vitamin C: Intravenous (IV) Vitamin C is sometimes administered to support the immune system during specific medical treatments or to promote wound healing in patients who can't take supplements by mouth. It's always used under strict medical supervision.
- Vitamin K: This vitamin is crucial for blood clotting. Newborns have low levels naturally, so a Vitamin K shot is standard procedure to prevent a rare but serious bleeding disorder.
This infographic shows the core safety principles that must be interconnected for any injectable vitamin therapy to be considered safe.
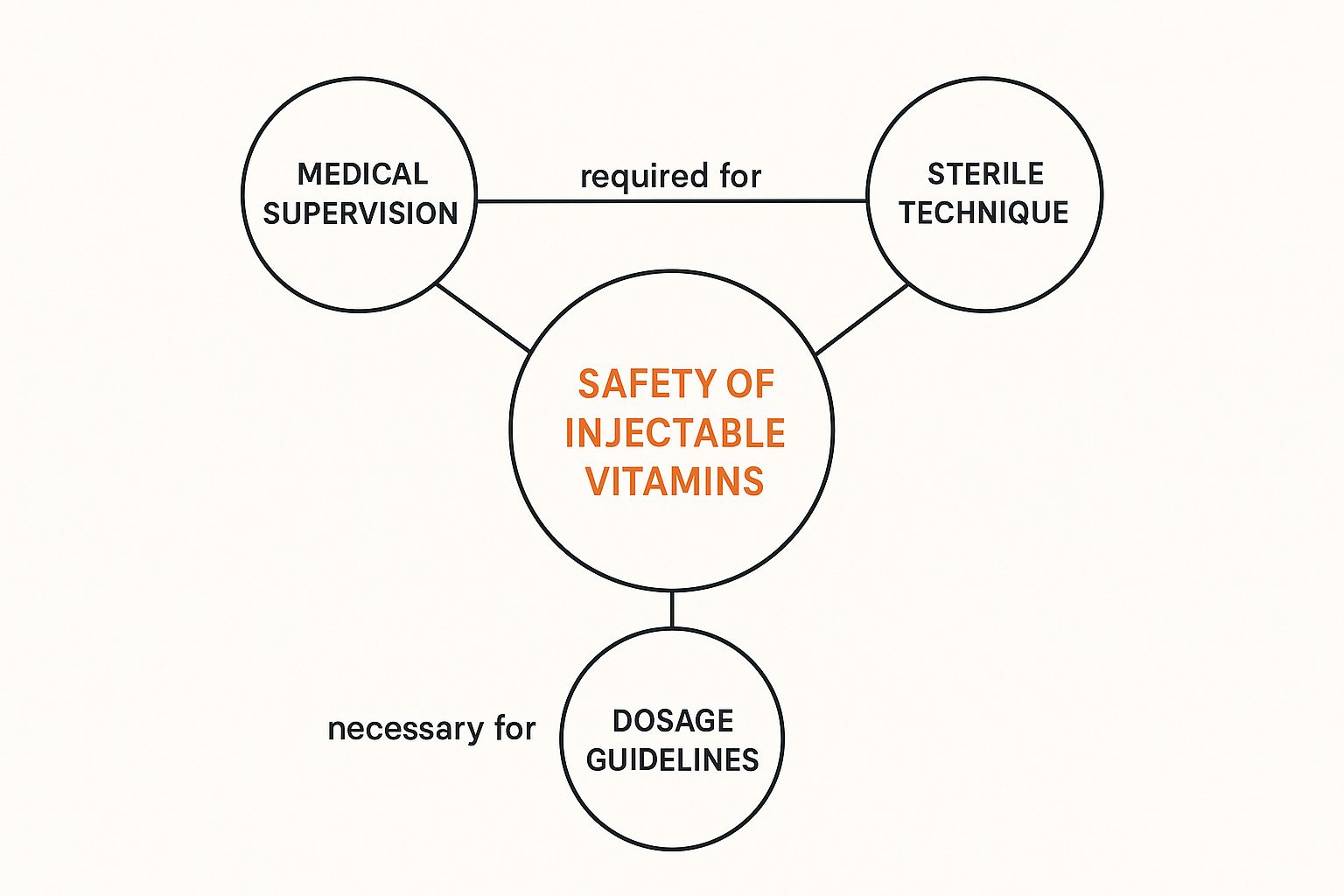
The image highlights that medical oversight, sterile practices, and correct dosing are not separate elements but parts of a single system. A breakdown in one area puts the entire treatment at risk. If you are interested in exploring the different formulations available under medical guidance, you can view our selection of injectable vitamin products.
Specialized and Emergency Applications
Some injectable vitamins are kept for specific, and often urgent, medical situations. The Vitamin K1 injection, for example, is a vital tool used in hospitals to counteract the effects of certain blood-thinning medications or to treat bleeding caused by a severe deficiency.
This specialized need has fueled considerable market growth. The global Vitamin K1 injection market is expected to reach $500 million by 2025, with over 100 million units produced each year. You can read more research about the expanding Vitamin K1 injection market to understand its clinical importance. Ultimately, the decision to use any of these powerful treatments is made by a qualified medical professional who can weigh the benefits against the risks for your unique health situation.
Who Actually Benefits From Injectable Vitamins?
While injectable vitamins for humans have gained traction in wellness clinics, their real power is unlocked for specific medical situations, not as a routine boost for healthy people. For most individuals with a varied diet, oral vitamins do the job just fine. However, for some, injections are not just an alternative—they are a clinical necessity. The key is to distinguish between genuine health needs and clever marketing.
Individuals With Malabsorption Disorders
The most straightforward case for vitamin injections is for people whose bodies can't properly absorb nutrients through their digestive systems. Think of their gut as a blocked filter—no matter how many oral supplements you introduce, very little can pass through to the bloodstream.
This is a reality for people with conditions like:
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune response to gluten that damages the small intestine, severely hindering nutrient absorption.
- Crohn's Disease: A form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) causing chronic inflammation along the digestive tract.
- Gastric Bypass Surgery: Patients whose digestive anatomy has been altered often need injectable vitamins for life to get essential nutrients.
- Atrophic Gastritis: This condition involves chronic inflammation of the stomach lining, which compromises the production of stomach acid and a protein called intrinsic factor, both essential for absorbing vitamin B12.
For these individuals, an injection completely bypasses the faulty digestive route, delivering vital nutrients directly into the bloodstream where they can be used.
Those With Specific Diagnosed Deficiencies
Beyond general absorption issues, some conditions interfere with the body's ability to process a single, specific vitamin. The classic example is pernicious anemia, an autoimmune disorder where the body fails to make the intrinsic factor needed to absorb vitamin B12 from food. Lifelong B12 injections are the standard, life-saving treatment for these patients, protecting them from severe and potentially permanent neurological damage.
Similarly, a person with a severe vitamin D deficiency that doesn't improve with high-dose oral supplements might need injections to bring their levels back to normal and safeguard their bone health.
Understanding the Market vs. Medical Need
The wellness industry has fully embraced injectable vitamins, fueling a massive market. The global vitamin market, which includes everything from injections to pills and fortified foods, reached a value of US$ 7.12 billion in 2024. Projections show it climbing to US$ 12.34 billion by 2032. You can read more about the global vitamin market trends to understand the full scope of this growth.
While this expansion reflects a broad interest in health, it’s important to remember that injectable vitamins serve a critical medical purpose for those who truly cannot absorb nutrients otherwise. They are a powerful tool for a specific group of people, not a universal wellness shortcut. A healthy person with a functional digestive system gains little to no extra benefit from an injection compared to a balanced diet and standard oral supplements. Any decision to use them should be driven by a medical diagnosis, not passing trends.
Safety Risks And Red Flags You Must Know
While they offer targeted benefits in the right situations, injectable vitamins for humans are powerful medical treatments that come with real risks. They are not a casual wellness add-on and should never be used without a clear understanding of the potential dangers. Just because a substance is a "vitamin" doesn't mean it's harmless when delivered in a concentrated, injectable form. A core principle to remember is that these treatments require professional administration and oversight for a reason.
The Dangers of Toxicity and Overdosing
One of the biggest risks is vitamin toxicity. It's a common myth that you can't overdose on vitamins, but this is dangerously false, especially with fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Unlike water-soluble vitamins (like B and C), which your body can easily flush out in excess, fat-soluble vitamins can build up in your tissues and organs. An improperly administered high dose of Vitamin D, for example, can lead to hypercalcemia—a condition where there's too much calcium in the blood—which can weaken bones and damage the kidneys and heart.
Even water-soluble vitamins aren't entirely risk-free at extreme levels. It is critical that dosing is managed by a healthcare provider who understands your specific health profile and needs. They can ensure you receive a therapeutic dose without crossing the line into a dangerous surplus.
To help you understand the safety landscape, the table below outlines the risks and precautions associated with common injectable vitamins.
| Risk Level | Common Side Effects | Contraindications | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Pain or redness at the injection site, mild muscle soreness, temporary flushing (Niacin). | Known allergies to specific vitamins. | Always administered by a qualified professional in a sterile environment. Ensure proper hydration. |
| Medium | Nausea, headache, dizziness (high-dose B vitamins). Hypercalcemia symptoms (Vitamin D): fatigue, bone pain. | Kidney disease, heart conditions, history of high calcium levels. Pregnancy or breastfeeding without doctor approval. | Pre-treatment blood work to check for deficiencies and existing conditions. Dosing based on individual needs, not generic protocols. |
| High | Severe hypercalcemia (Vitamin D), nerve damage (excess Vitamin B6), blood clotting issues (Vitamin K). Risk of serious infection from unsterile administration. | Active cancer treatment (some antioxidants), severe kidney or liver failure, blood clotting disorders. | Requires a thorough medical consultation and ongoing monitoring. Avoid "IV drip bars" without licensed medical staff. |
This table highlights why a one-size-fits-all approach is unsafe. A qualified provider will assess these factors before recommending any treatment.
Recognizing Red Flags in Treatment
Knowing the warning signs of an unsafe provider or situation is your best defense. Administering injectable vitamins requires more than just a needle; it demands strict adherence to medical standards. Here are some critical red flags to watch for:
- Lack of Medical Consultation: If a clinic or service offers injections without a thorough health assessment, including a review of your medical history and blood work, walk away.
- Non-Sterile Environment: The procedure must happen in a clean, clinical setting. Any signs of poor hygiene are a major warning. Unsterile techniques can lead to serious infections, abscesses, or even bloodborne diseases.
- Pressure to Buy Packages: Aggressive sales tactics or pressure to buy multiple sessions upfront often prioritize profit over your health and safety.
- Vague or Miracle Claims: Be wary of providers promising that injections can cure serious diseases or offer universal benefits without evidence to back it up.
Administering these treatments also requires awareness of potential interactions. For instance, some injectable antioxidants can affect how other medications work. If you're interested in learning about a specific antioxidant, you can read our guide on glutathione injections. Ultimately, your safety depends on a transparent and professional approach from a qualified medical team that can account for these complexities.
Finding Safe, Legitimate Injectable Vitamin Treatment
If you're thinking you might have a vitamin deficiency, your first step should always be a proper medical evaluation, not a quick trip to a wellness spa. While the idea of a fast fix is tempting, getting legitimate injectable vitamins for humans means working with the healthcare system to make sure the treatment is both necessary and safe.
The absolute starting point is to consult with a qualified healthcare provider, like a medical doctor (MD), doctor of osteopathic medicine (DO), or a nurse practitioner. This professional will perform a complete health assessment, looking at your medical history, current symptoms, and diet. Most importantly, they will order blood work to see if a deficiency is actually present. Without blood tests, any suggestion for vitamin shots is purely guesswork.
Medical Clinics Versus Wellness Centers
Knowing the difference between a medical clinic and a wellness or IV drip bar is key to your safety.
- Medical Clinics: These are run by licensed medical professionals who diagnose and treat documented health conditions. They use injectable vitamins based on confirmed clinical needs from lab tests.
- Wellness Centers: These often promote lifestyle and cosmetic perks. They might not have strict medical oversight and may not require blood work before administering treatments.
A trustworthy medical provider will always take the time to explain why an injection is a better option for you than oral supplements. They'll discuss the specific vitamin, the dosage based on your lab results, and how long you can expect the treatment to last. For more details on the importance of safety with self-administered therapies, which must always be done under medical guidance, you can check out our guide on hormone and testosterone injection safety.
Key Questions for Your Provider
To make sure you're getting the right care, don't be afraid to ask direct questions:
- What do my lab results show?
- Why are oral supplements not the right choice for me?
- What are the potential side effects of this injection?
- How will we track my progress and vitamin levels?
This screenshot from the Mayo Clinic highlights the potential risks and side effects of IV therapy, showing why professional medical supervision is so important.
The information confirms that even routine procedures have risks that need to be managed by trained professionals who know how to handle complications.
When it comes to cost, medically necessary injectable vitamin treatments are sometimes covered by insurance, but this varies. Out-of-pocket costs can differ greatly, but be cautious of providers who push expensive, multi-session packages without a clear medical reason. Real medical care puts your health first, not sales. If a provider dodges your questions, dismisses your concerns, or pressures you into a treatment plan, it's a major red flag. Your best move is to seek a second opinion.
Making Smart Decisions About Injectable Vitamin Therapy
When considering injectable vitamins for humans, it’s essential to be an active, informed participant in your own healthcare. Making smart decisions means you can protect both your health and your wallet. The goal is to carefully weigh the potential upsides against the risks and costs, ensuring any treatment you pursue is a real solution, not just an expensive placebo.
Your journey should always start with a qualified healthcare professional who relies on evidence, not just the latest wellness trends. A thorough evaluation, including blood work, is the only way to confirm a deficiency and decide if injections are the right path for you. This partnership with your provider is the cornerstone of safe and effective therapy.
A Practical Checklist for Evaluating Treatment
Before you agree to any injectable vitamin therapy, it's a good idea to take a step back and use a simple, objective checklist. Think of this as your due diligence to make sure the treatment truly matches your health needs. A reputable provider will encourage this thoughtful approach, whereas one more focused on sales might try to rush you.
Use these points to guide your evaluation:
- Confirmed Medical Need: Has a blood test definitively shown a deficiency? Have you discussed why oral supplements aren't a good alternative for your specific situation?
- Realistic Expectations: Do you have a clear understanding of what the treatment can and cannot achieve? Are the promised benefits based on medical science or on vague claims about general wellness?
- Clear Treatment Plan: Is there a defined plan that specifies the vitamin, dosage, and frequency? Does it include follow-up testing to track your progress and establish an end date for the therapy?
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Do you know the full cost of the treatment? Do the expected health improvements justify the expense, particularly if your insurance doesn't cover it?
Key Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
Having a productive conversation with your provider is vital. Asking the right questions helps you understand the "why" behind their recommendations. A trustworthy professional will always welcome your inquiries and give you clear, easy-to-understand answers.
Here are some crucial questions to ask during your consultation:
- Based on my lab results, why is this specific injectable vitamin necessary for me?
- What are the most common side effects, and what warning signs should I look out for?
- How will we measure whether this treatment is working?
- Are there any potential interactions with my current medications or other health conditions?
- When can we re-evaluate my progress to see if I can switch to oral supplements?
Monitoring Your Progress and Knowing When to Stop
Proper vitamin therapy isn't meant to be a lifelong commitment. A crucial part of the process is monitoring its effects. Follow-up blood tests are non-negotiable—they offer objective proof of whether the treatment is delivering results. If your vitamin levels aren't improving, or if they've returned to a healthy range, it’s time to review the plan with your doctor.
It's also important to distinguish between a genuine physiological improvement and a placebo effect. While feeling better is wonderful, it must be supported by measurable data. For many people, the ultimate goal is to correct the deficiency so they can maintain healthy levels through diet or less invasive oral supplements. Being an informed patient allows you to confidently explore your options, sidestep unnecessary treatments, and invest in solutions that provide real, lasting health benefits.
If you're ready to take a medically-guided approach to your health, Elite Bioscience offers a secure platform to connect with medical professionals, receive a valid prescription based on your needs, and access third-party tested therapies from the comfort of your home.







