As men get older, it's a completely normal part of life for testosterone levels to gradually decline. Your peak years for testosterone are typically in your late teens and early 20s. After you hit 30, it’s common to see a slow, steady drop of about 1% per year. This isn't a sign of a medical problem—it's just a natural part of the aging process.
Decoding the Testosterone Levels by Age Chart
Think of testosterone like the horsepower of a brand-new engine. It’s at its absolute peak performance fresh off the line, and while it might lose a little bit of that raw power over many years, it remains a highly functional and reliable engine for the long haul. A testosterone chart is like a diagnostic snapshot of that journey, giving you reference ranges to see where your levels fall compared to other guys in your age group. But remember, these numbers are guidelines, not rigid rules.
This visual guide gives you a clear look at the general trend of how average testosterone levels shift downward as men age.
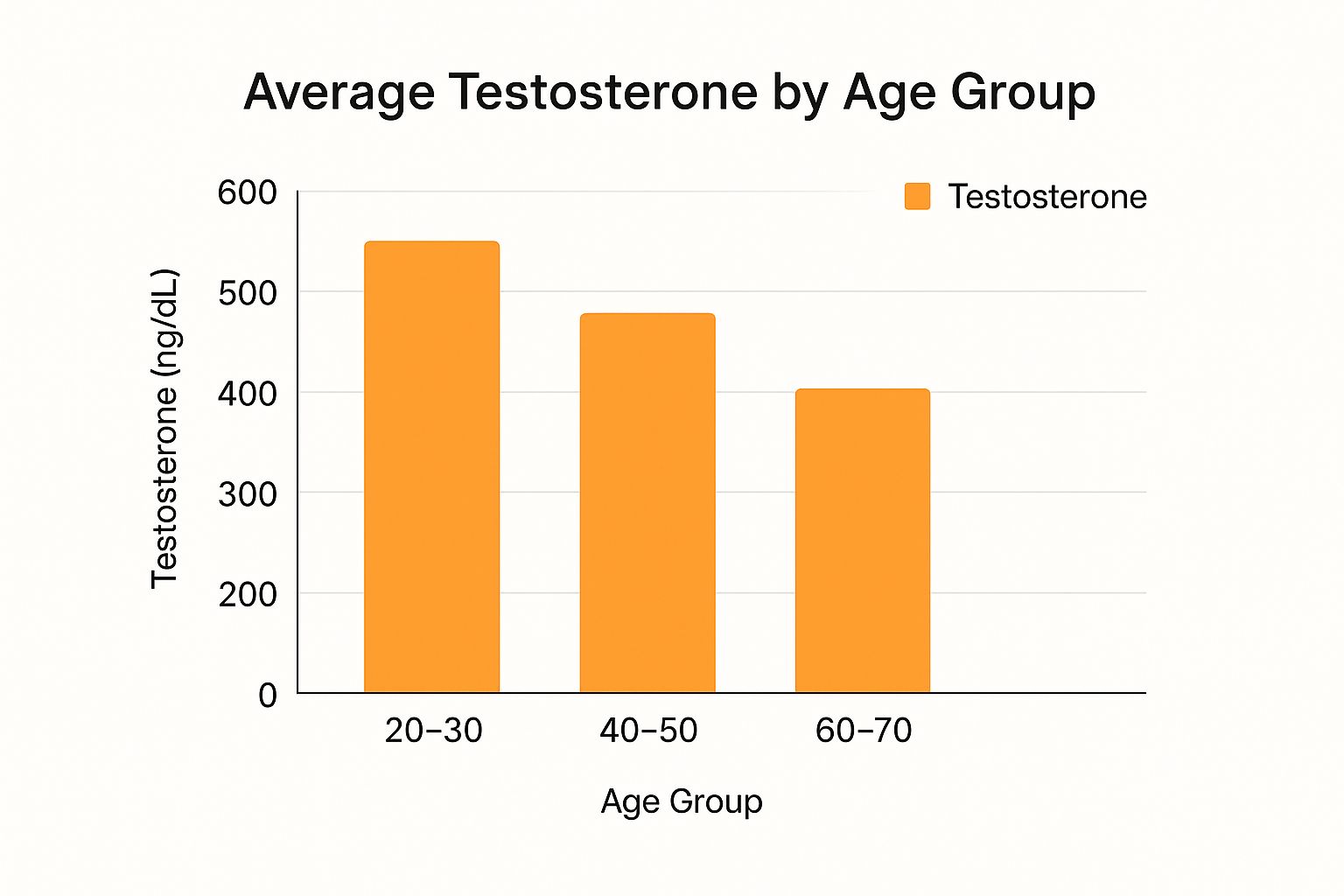
As the chart makes plain, what's considered a typical testosterone level for a man in his 20s is quite a bit different from what's normal for a man in his 60s.
What Is a Normal Testosterone Level for My Age?
Figuring out what's "normal" can be a little tricky. Standard lab reports often give a huge reference range, usually somewhere between 300 to 1,000 ng/dL for all adult men. The problem with such a wide range is that it doesn't really capture the nuances of how aging affects these levels. What really matters is understanding the typical range for your specific age bracket, as that provides a much more relevant benchmark.
Thankfully, recent research is helping us narrow things down. A 2022 study, for instance, established more precise age-specific ranges. It found that men aged 20–24 had normal total testosterone between 409–558 ng/dL. Fast forward to the 40–44 age group, and that typical range shifted down to 350–473 ng/dL, which confirms that slow and steady decline. You can discover more insights from this age-related testosterone study to see the full data.
The most important thing to remember is that your personal "normal" is unique to you. A number that causes zero symptoms for one person might be problematic for another, even if both fall within that standard lab range.
To give you an even clearer picture, here’s a more detailed breakdown of average total testosterone levels across different stages of life. This table can help you make sense of what you might expect to see on a lab report.
Average Total Testosterone Levels by Age Group
This table presents typical reference ranges for total testosterone in adult males, broken down by decade, to help readers quickly find information relevant to their age.
| Age Group (Years) | Average Total Testosterone Range (ng/dL) | Average Total Testosterone Range (nmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 20–29 | 400–900 | 13.9–31.2 |
| 30–39 | 350–800 | 12.1–27.7 |
| 40–49 | 300–700 | 10.4–24.3 |
| 50–59 | 250–600 | 8.7–20.8 |
| 60+ | 200–500 | 6.9–17.3 |
Ultimately, these charts and tables are fantastic tools for starting a conversation about your health. They offer a solid framework for understanding potential changes over time, but the most critical factor is always how you actually feel day-to-day.
The Natural Ebb and Flow of Testosterone Production

To really make sense of a testosterone levels by age chart, you have to appreciate the lifelong story of this vital hormone. Its journey isn't a flat, boring line. Instead, it’s a dynamic curve that perfectly mirrors the different stages of a man's life—think of it as a natural lifecycle with distinct chapters, each with its own purpose.
This story kicks off with a massive surge during puberty. This is when testosterone production goes into overdrive, fueling the development of secondary male characteristics like a deeper voice, muscle growth, and body hair. This period literally builds the foundation for masculine health for decades to come.
The Peak Years and The Inevitable Decline
After that powerful developmental surge, testosterone levels hit their absolute peak. For most guys, production is at its highest in the late teens and early twenties, driving peak physical performance, energy, and libido. The body sustains this hormonal high point for several years, representing a man’s biological prime.
But nothing stays at its peak forever.
Starting around age 30, production begins a slow, predictable decline. It’s not a sudden crash, but more of a gradual tapering off. This gentle descent is a completely normal part of aging, not some immediate red flag you need to worry about.
The real takeaway here is that this change is constant and totally expected. Viewing this hormonal shift as a natural progression, rather than a deficiency, helps you see the numbers on a testosterone levels by age chart with a much healthier and more realistic perspective.
This gradual slide is remarkably consistent. Production hits its zenith during adolescence, around age 17, and stays high through the 20s and 30s. Then, from about age 40 onward, levels begin to decrease by an average of 1% per year.
This means that by age 70, a man’s testosterone production might be 30% lower than it was in his prime. This fact really highlights the slow and steady nature of this change. You can get more details on how aging affects testosterone directly from Harvard Health Publishing.
Understanding this natural ebb and flow is everything. It gives you the "why" behind the numbers, helping you interpret your own levels with the right context and without jumping to conclusions.
Why Modern Lifestyles Are Tanking Testosterone Levels
The slow, natural decline of testosterone with age is a biological fact, but it doesn't tell the whole story. A strange and somewhat alarming trend has surfaced: younger men today often have lower testosterone than men of the same age just a generation or two ago. This tells us that the numbers on a testosterone levels by age chart are being pushed down by something more than just birthdays.
This isn’t a statistical blip. It points directly to how our modern environment and day-to-day habits are impacting male hormones. Think of your endocrine system like a finely tuned engine. It's built to run smoothly for decades, but it needs the right fuel (nutrition), regular upkeep (exercise), and proper downtime (sleep). When you skimp on any of these, the engine's performance is going to suffer.
Hard data backs this up. A study looking at men in the United States between 1999 and 2016 found a significant and steady drop in testosterone levels among young adults and even teenagers—including those with a healthy body weight. This is a clear signal that factors beyond aging are at work. You can read the full findings on this generational hormone shift to see just how widespread the issue has become.
The Key Lifestyle Culprits
So, what parts of modern life are throwing a wrench in the works? The main offenders are chronic stress, terrible sleep, sitting around all day, and eating nutrient-stripped diets. Any one of these can mess with hormone production, but when you combine them, you create a perfect storm for hormonal imbalance.
Take chronic stress, for example. It cranks up cortisol, the body’s main stress hormone. Cortisol and testosterone have a seesaw relationship—when one goes up, the other tends to go down. This is an ancient survival switch, telling your body to focus on immediate threats instead of long-term projects like building muscle or maintaining libido.
Sleep is just as critical. Your body produces the majority of its testosterone during deep REM sleep, so skimping on it directly sabotages the process. Just one week of sleeping only five hours a night can slash a young man’s testosterone by a staggering 10-15%.
Your daily choices are casting a vote for or against your hormonal well-being. The food you eat, the sleep you get, and the stress you manage are not passive activities—they are active inputs that directly regulate your body's hormonal output.
The Impact of Diet and Inactivity
What we eat and how little we move also play a huge role in this hormonal decline.
Nutrient-Poor Diets: A diet loaded with processed foods, sugar, and bad fats can cause insulin resistance and inflammation. Both are notorious for suppressing testosterone production. Meanwhile, key micronutrients for making hormones, like zinc and Vitamin D, are often missing from these diets.
Sedentary Habits: A lack of physical activity, especially strength training, means the body never gets the signal to produce more testosterone. Exercise is a powerful trigger for hormonal health and muscle growth. Without it, the system just stays idle.
Ultimately, knowing these factors is empowering. While you can't turn back the clock, you have a massive amount of control over the lifestyle variables that determine where your own T levels will land on the chart.
Connecting the Numbers to How You Actually Feel

A testosterone levels by age chart is a fantastic map, but the numbers alone don't tell the whole story. The most important part of this equation is you—your energy, your mood, and your overall sense of well-being. A lab report showing a number like 450 ng/dL means very little if you’re constantly battling fatigue and brain fog.
This is where bridging the gap between data and daily life becomes critical. Think of it this way: the chart shows you the average speed limit for your age group, but how your personal "engine" runs at that speed is what truly matters. Symptoms are your body's check-engine light, signaling that something under the hood might need attention, even if you're technically still on the road.
Recognizing these signals early is key. Persistent fatigue that doesn't improve with rest, a nagging low mood, or difficulty concentrating aren't just random signs of a tough week. They can be subtle but direct indicators that your hormonal balance is off.
Linking Symptoms to Your Levels
While you should never try to self-diagnose, understanding how symptoms often correlate with certain testosterone ranges is incredibly empowering. It helps you identify patterns in your own health. For instance, a man might first notice a dip in his energy when his levels drop, while more pronounced symptoms like low libido may appear later on.
Clinical observations have shown that specific symptoms often become more common as testosterone levels fall below certain thresholds.
- Reduced Energy Levels: This is often one of the first signs, typically appearing when total testosterone dips below 15 nmol/L (around 430 ng/dL).
- Weight Gain & Mood Changes: Increased body fat and feelings of low mood or irritability frequently emerge when levels fall under 10 nmol/L (around 288 ng/dL).
- Erectile Dysfunction: Issues with erectile quality often become a real concern when levels drop below 8 nmol/L (around 230 ng/dL).
This knowledge transforms abstract numbers into something tangible you can discuss with a healthcare professional. Instead of just saying "I feel off," you can have a much more productive conversation about specific patterns you've noticed.
Your personal experience is the most valuable piece of data you have. A lab number is a single snapshot in time, but how you feel day-to-day provides the full context needed for a true assessment of your hormonal health.
The table below offers a clearer look at how common symptoms often align with different testosterone ranges. This isn't a diagnostic tool, but it can be a useful guide to help you recognize potential warning signs.
Symptom Correlation with Testosterone Levels
This table illustrates the relationship between declining testosterone levels and the emergence of specific symptoms, based on clinical observations.
| Symptom | Commonly Associated Total Testosterone Level |
|---|---|
| Persistent Fatigue / Low Energy | Below 450 ng/dL (15.6 nmol/L) |
| Brain Fog / Poor Concentration | Below 400 ng/dL (13.9 nmol/L) |
| Low Mood / Irritability | Below 350 ng/dL (12.1 nmol/L) |
| Decreased Libido / Sex Drive | Below 300 ng/dL (10.4 nmol/L) |
| Loss of Muscle Mass | Below 250 ng/dL (8.7 nmol/L) |
If these symptoms feel familiar, it may be time to act. Exploring science-based ways to support your hormones can be a great first step, and you can learn more about the secrets to boosting testosterone levels to see what strategies might work for you. Ultimately, this knowledge empowers you to take control and seek the right medical advice when necessary.
How to Get an Accurate Testosterone Reading
Getting a blood test for testosterone seems simple enough, but nailing down a truly accurate number takes a bit more planning than just showing up at the lab. Your testosterone levels aren't a flat line; they naturally rise and fall throughout the day. Because of this, timing is everything.
Testosterone production hits its peak in the early morning while you’re asleep. That means your levels are at their absolute highest right after you wake up.
To capture your true baseline, a blood draw should always be scheduled between 7 AM and 10 AM. A test taken later in the afternoon could give you an artificially low number, painting an inaccurate picture of your hormonal health.
Locking in that morning appointment is the non-negotiable first step. But other temporary factors can also throw off your results, so a little prep work is essential to get a clean reading.
Optimizing Your Blood Test Conditions
Think of a testosterone test as a single snapshot in time. You want that picture to reflect a normal, rested day—not a moment of unusual stress, sickness, or exhaustion. A few simple preparations can make all the difference in ensuring the reading is as accurate as possible.
Before your test, it's smart to account for a few things that can temporarily skew your numbers:
- A Full Night's Sleep: Your body manufactures the most testosterone during deep REM sleep, so a night of tossing and turning can seriously drag down your morning reading. Aim for 7-9 hours of solid, quality sleep the night before.
- Recent Illness: Being sick puts your body under a huge amount of stress, which can hit the brakes on testosterone production. It’s always best to wait until you've fully recovered before getting your levels checked.
- Intense Exercise: A monster workout the day before your test can temporarily tank your testosterone. Stick to light activity or just take a rest day to avoid this.
Understanding the Different Types of Testosterone
When you get your lab report back, you'll probably see a few different numbers. The main one is total testosterone, which measures every last bit of testosterone flowing through your bloodstream. The thing is, not all of it is actually usable by your body.
A big chunk of it is tightly bound to proteins, mostly Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG). Only the unbound portion, known as free testosterone, and the weakly bound portion (called bioavailable testosterone) can actively get into your cells and do their jobs.
For a complete hormonal picture, your doctor might also check your Luteinizing Hormone (LH), which is the signal the brain sends to the testes telling them to make testosterone. Understanding these distinctions is crucial, and so is consistent lab work. That’s why monitoring is important for testosterone replacement therapy and for establishing a reliable baseline in the first place.
Actionable Steps for Supporting Healthy Hormones

While you can’t stop the clock on aging, you have a surprising amount of control over the lifestyle factors that determine where you land on the testosterone chart. Supporting healthy hormones isn't about chasing quick fixes. It’s about building a foundation of smart, sustainable habits that deliver real, lasting results for your overall vitality.
Think of your body as a high-performance engine. To keep it running smoothly, you need to give it premium fuel, put it through its paces, and allow for proper downtime and maintenance. The exact same principle applies to your endocrine system.
Prioritize Resistance and Strength Training
One of the loudest signals you can send your body to produce more testosterone is resistance training. Lifting weights creates a powerful demand for muscle repair and growth, which in turn flips on the hormonal switches needed to get the job done.
Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are king here. They engage multiple large muscle groups at once, maximizing the hormonal trigger. The key is consistency and focusing on progressive overload—gradually increasing the weight, reps, or intensity over time to keep challenging your body.
Master Your Nutrition and Micronutrients
Your diet provides the raw materials your body needs to manufacture hormones. A balanced intake of proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbs is the bedrock, but a few specific micronutrients play a starring role.
- Zinc: This mineral is absolutely essential for testosterone synthesis. You can find it in foods like red meat, shellfish, and seeds.
- Vitamin D: Often called the "sunshine vitamin," Vitamin D actually functions more like a hormone in the body and is vital for keeping testosterone levels in a healthy range.
- Healthy Fats: Cholesterol is the precursor molecule to testosterone, making healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil completely indispensable.
Managing the stress hormone, cortisol, is just as important as boosting testosterone. Chronic stress keeps cortisol elevated, which actively suppresses testosterone production in a hormonal seesaw effect.
Optimize Sleep and Reduce Stress
The vast majority of your daily testosterone is produced while you sleep. Consistently getting 7-9 hours of quality, uninterrupted sleep is non-negotiable for hormonal balance. Skimping on sleep directly sabotages this critical production window.
At the same time, you need to find effective ways to manage daily stress, whether that's through mindfulness, hitting the gym, or losing yourself in a hobby. Lowering cortisol allows your body to shift its resources back toward optimal hormone production. For a deeper dive, explore our guide on how to increase testosterone levels naturally with proven strategies.
Your Questions Answered: Digging Deeper into the Numbers
A testosterone levels chart is a great starting point, but it naturally brings up more specific questions. Let's break down some of the most common things men wonder about when they start looking into their hormonal health.
Does Test Timing Matter?
Yes, and it matters a whole lot. Your testosterone levels aren't static throughout the day; they follow a natural rhythm, hitting their absolute peak in the morning. Think of it like your body spending the night on a production line, getting everything ready for the day ahead.
That peak window is usually between 7 AM and 10 AM. A blood draw in the afternoon could catch you at a low point, giving you a number that looks artificially low and doesn't reflect your true baseline. This is exactly why your doctor will almost always insist on an early morning test—it's the only way to get an accurate snapshot.
Can I Have Symptoms with "Normal" Results?
Absolutely. This is probably one of the most frustrating situations a man can find himself in, and it's incredibly common. The so-called "normal" range you'll see on a lab report is often a massive span, typically from 300 to 1,000 ng/dL, which lumps together men of all ages.
You could easily land at the low end of that spectrum. While a lab technician might stamp it "normal," your body might feel anything but. This is precisely why how you feel is just as important, if not more so, than the number on the page.
Your symptoms are a vital piece of the puzzle. A number that’s perfectly fine for one person could be the source of significant issues for another. It highlights the need to look beyond a generic lab reference range and listen to what your body is telling you.
Is TRT My Only Option?
Not at all. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a specific medical treatment, not a first-line solution for slightly lower levels. It's typically reserved for men who have a clinical diagnosis of hypogonadism and are dealing with significant, persistent symptoms that impact their quality of life.
For many guys, the most powerful first step is making smart lifestyle adjustments. You'd be amazed at what focusing on the fundamentals can do. Things like a nutrient-dense diet, consistent strength training, nailing 7-9 hours of quality sleep, and getting a handle on stress can make a world of difference. These are the pillars of health that can often restore your levels naturally, without any need for medical intervention.
At Elite Bioscience, we give you the resources and therapies to take back control of your health. Our process is straightforward, making it simple to get expert medical guidance and effective treatments delivered right to your door. Explore your options and start your journey to optimized vitality today. https://elitebioscience.co







